Lavanya
Jan 6, 2026
Introduction
WEEE compliance represents one of the most critical regulatory frameworks that manufacturers and distributors must navigate today. The Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive establishes mandatory WEEE compliance requirements that fundamentally reshape how manufacturers approach electrical and electronic waste management across Europe and beyond.
For any organization selling electrical or electronic equipment in EU markets, achieving WEEE compliance is non-negotiable. This comprehensive guide to WEEE compliance breaks down the complex regulatory landscape, examining extended producer responsibility obligations, compliance costs, reporting requirements, and practical strategies for implementing WEEE compliance across your operations.
Whether you're a global electronics manufacturer entering European markets for the first time or an established producer optimizing your WEEE compliance operations, understanding WEEE compliance requirements is essential for protecting your business while managing environmental responsibility. The consequences of failing to maintain proper WEEE compliance can be severe, ranging from substantial financial penalties to supply chain disruption and reputational damage. Organizations that leverage AI-native compliance automation can significantly reduce the manual burden of managing multi-country WEEE obligations while maintaining continuous audit-ready documentation across all jurisdictions.
This blog provides everything you need to understand and implement WEEE compliance: from initial registration requirements through ongoing reporting obligations, collection infrastructure development, and advanced compliance optimization strategies.
We'll explore how to achieve WEEE compliance efficiently, navigate country-specific variations in WEEE compliance requirements, and position your organization for success in this evolving regulatory environment.
Understanding WEEE Compliance and Extended Producer Responsibility
WEEE compliance refers to adherence with the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (Directive 2012/19/EU and amended versions), which establishes legal requirements for managing electrical and electronic waste across European Union member states. WEEE compliance is mandatory for any manufacturer or distributor placing electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) on the market.
WEEE compliance requirements encompass multiple interconnected obligations:
Registration with national authorities and compliance schemes
Declaration of products placed on the market (PoM)
Establishment of collection infrastructure
Funding of treatment and recycling operations
Annual reporting on collection and recycling activities
Proper disposal of electrical and electronic waste
Hazardous substance management and de-pollution
WEEE compliance is not a one-time certification but an ongoing operational requirement. Manufacturers must maintain continuous WEEE compliance across all markets where products are sold, adapting to regulatory changes and evolving collection targets. Staying ahead of these shifting obligations requires robust regulatory intelligence and horizon scanning—proactively monitoring legislative updates across EU member states so your compliance posture is never reactive.
How to Achieve WEEE Compliance: The Extended Producer Responsibility Model
The cornerstone of WEEE compliance is the principle of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR). Achieving WEEE compliance fundamentally revolves around accepting responsibility for your products throughout their entire lifecycle—not just the manufacturing and sales phases. In practical terms, EPR compliance means that producers bear direct financial and operational accountability for collection, treatment, and recycling—obligations that scale with every unit placed on the market. For a broader view of how extended producer responsibility frameworks apply across product categories, see Certivo's EPR framework overview.
Extended producer responsibility obligations require manufacturers to bear financial and operational responsibility for:
Collection of end-of-life products
Safe transportation to authorized treatment facilities
Proper de-pollution of hazardous materials
Material recovery and recycling processes
Documentation and reporting of all activities
How to achieve WEEE compliance requires integrating EPR principles into core business operations. This means designing products with end-of-life management in mind, establishing collection infrastructure, funding treatment operations, and maintaining detailed compliance records.
Why Producer Responsibility Obligation Creates Market Incentives
The producer responsibility obligation transforms waste management economics. When manufacturers directly bear the costs of recycling, they gain powerful incentives to:
Reduce material consumption and complexity
Eliminate hazardous substances beyond regulatory minimums
Design products for easier disassembly and material recovery
Minimize packaging and packaging waste
Optimize logistics for collection and reverse distribution
This market-based approach drives innovation toward circular economy models, where materials are recovered and reused rather than discarded. Manufacturers embedding design-for-compliance PLM workflows into product development can reduce material complexity and hazardous substance content at the design stage—directly lowering eco-contribution fees and simplifying end-of-life treatment.
WEEE Compliance Requirements by Country and Jurisdiction
EU WEEE Compliance Requirements Framework
The European Union establishes baseline WEEE compliance requirements through the WEEE Directive, but implementation varies significantly across member states. Manufacturers must understand both EU-wide baseline requirements and country-specific implementations to maintain proper WEEE compliance across all markets.
Mandatory Registration for WEEE Compliance
Every manufacturer achieving WEEE compliance must register with designated national authorities in each EU country where electrical and electronic equipment is placed on the market. WEEE compliance requirements for registration include:
Registration Components:
Company identification and contact information
Product categories being placed on market
Estimated quantities of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) distributed
Proof of financial provision for waste management through compliance scheme membership or individual system
Registration Timeline: Registration must occur before placing products on the market. Failure to achieve initial WEEE compliance registration can result in:
Sales restrictions or product blocking at borders
Regulatory fines ranging from thousands to millions of euros
Exclusion from distribution channels
Mandatory back-fees and penalty interest
Put on Market (PoM) Declarations and WEEE Compliance
Manufacturers must declare the quantity of electrical and electronic equipment they "put on the market"—the total amount of products made available for distribution within a specific territory. How to achieve WEEE compliance includes accurate PoM declarations as a foundational element.
PoM declarations enable:
Baseline establishment for calculating WEEE compliance obligations
National authority tracking of product flows and market trends
Determination of producer compliance scheme fees
Producer accountability for collection and recycling targets
Regulatory assurance that manufacturers are maintaining proper WEEE compliance
Accurate PoM data depends on granular BOM-level material mapping—knowing the exact weight, material composition, and category classification of every product variant placed on each national market. Without this foundation, WEEE reporting errors and fee miscalculations become systemic.
UK WEEE Compliance Requirements Post-Brexit
Following Brexit, the United Kingdom implemented its own WEEE compliance requirements framework, broadly aligned with EU standards but with distinct operational differences affecting WEEE compliance.
UK Producer Compliance Scheme Requirements
In the UK, manufacturers achieving WEEE compliance must join one of approximately 40 approved producer compliance schemes. These schemes function as intermediaries managing compliance obligations on behalf of members, similar to collective schemes in EU countries. Each WEEE compliance scheme in the UK handles registration, WEEE reporting submissions, and evidence note management on behalf of its members—making scheme selection a critical operational decision.
UK-Specific WEEE Compliance Requirements:
Membership in approved Producer Compliance Scheme
Annual WEEE compliance registration with scheme and authorities
Declaration of products placed on market (PoM)
Payment of annual compliance scheme fees
Participation in "in-store take-back" obligations for retailers
WEEE Product Categories and Classification
10 Primary WEEE Categories Affecting Compliance
The WEEE Directive establishes 10 primary product categories, each with distinct WEEE compliance requirements and recycling obligations. Accurate product classification is essential for maintaining WEEE compliance.
Category 1: Large Household Appliances
Products: Refrigerators, washing machines, dishwashers, cookers
WEEE compliance requirements: Recovery of CFC and hazardous coolants
Collection rate: 60-70% of products sold
Category 2: Small Household Appliances
Products: Microwave ovens, toasters, coffee makers, vacuum cleaners
WEEE compliance requirements: Safe removal of hazardous components
Lower per-unit compliance costs due to smaller size
Category 3: IT and Telecommunications Equipment
Products: Computers, printers, mobile phones, servers
WEEE compliance requirements: Secure data destruction, precious metal recovery
High value recovery (gold, silver, copper content)
Category 4: Consumer Electronics
Products: Televisions, home theater systems, DVD players, cameras
WEEE compliance requirements: Screen/monitor treatment, mercury removal
Growing category affecting many manufacturers
Category 5: Lighting Equipment
Products: Fluorescent tubes, LED bulbs, compact fluorescent lamps
WEEE compliance requirements: Mercury and rare earth element management
Requires specialized de-pollution processes
Category 6: Electrical and Electronic Tools
Products: Power drills, circular saws, electric lawn mowers
WEEE compliance requirements: Battery and motor recycling
Often classified as professional equipment with different WEEE compliance rules
Category 7: Toys, Leisure, and Sports Equipment
Products: Electric toys, video game consoles, sports watches
WEEE compliance requirements: Small battery management
Growing category with lower historical recycling rates
Category 8: Medical Devices
Products: Defibrillators, dialysis machines, X-ray equipment
WEEE compliance requirements: Biohazard decontamination
Specialized handling requirements affecting WEEE compliance approach
Manufacturers in the medical device sector face overlapping regulatory obligations beyond WEEE—see Certivo's medical device compliance management guide for additional considerations.
Category 9: Monitoring and Control Equipment
Products: Thermostats, smoke detectors, measuring instruments
WEEE compliance requirements: Radioactive material management
Specialized regulatory pathways for WEEE compliance
Category 10: Automatic Dispensers
Products: Vending machines, ATMs, fuel dispensers
WEEE compliance requirements: Mechanical hazard removal
Largest weight category affecting compliance fee calculations
Impact of Accurate Classification on WEEE Compliance
Misclassification creates compliance violations:
Incorrect WEEE compliance requirements application
Significant underpayment of compliance fees
Regulatory penalties and fines
Mandatory reclassification and backdated fee adjustments
Damage to compliance credibility
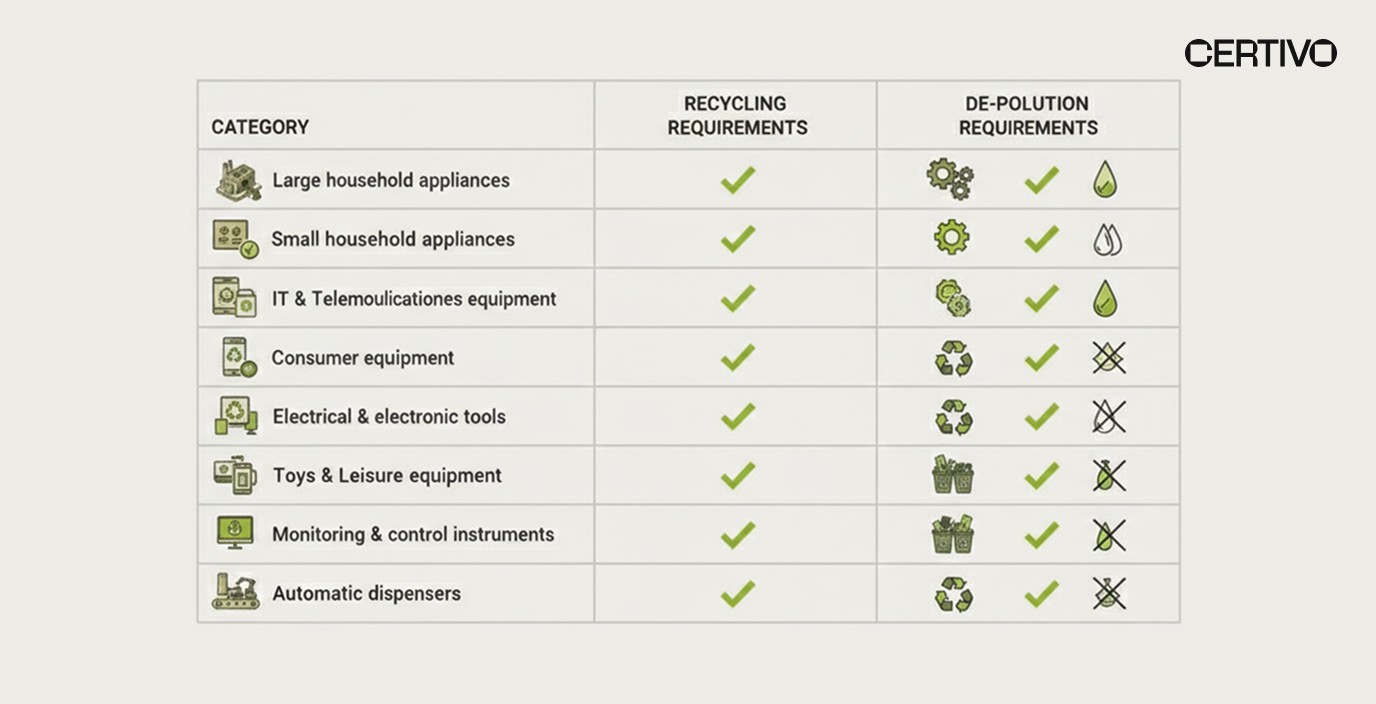
Collection and Recycling Targets Under WEEE Directive
Historical and Current Collection Targets Driving WEEE Compliance
The WEEE Directive establishes progressively challenging collection and WEEE compliance requirements:
Current Target Framework (2026+):
65-85% collection target of average electrical and electronic waste weight
Specific recycling targets for material recovery (75-95% by category)
Recovery targets for hazardous substance removal (85-95%)
Producer financial accountability when collection targets fall short
What Collection Targets Mean for WEEE Compliance
Collection targets create direct financial accountability affecting WEEE compliance:
When collective collection falls short of targets, producers collectively fund shortfalls
Manufacturers with higher market share bear proportionally higher contributions
Financial penalties apply for collective non-compliance with WEEE requirements
Producer responsibility obligations increase when collection performance declines
WEEE Compliance Costs and Fee Structures
Components of WEEE Compliance Costs
Registration Fees for WEEE Compliance
One-time WEEE compliance registration fees: €500-€3,000 per country
Annual WEEE compliance renewal fees: €200-€1,000
Critical for achieving initial WEEE compliance
Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO) Membership Fees
Annual membership fees enabling WEEE compliance through schemes: €1,000-€5,000
Flat rate component providing access to national compliance infrastructure
Essential for maintaining ongoing WEEE compliance
Eco-Contributions (Per-Unit Recycling Fees)
Primary cost driver for manufacturers maintaining WEEE compliance
Calculated based on:
Product weight (in kg)
Product category (1-10 from WEEE classification)
Member state where electrical and electronic equipment is sold
Material composition and hazardous content
Typical WEEE Compliance Cost Range:
Small consumer electronics (100g): €0.05-€0.30 per unit
Medium appliances (5kg): €1.00-€5.00 per unit
Large appliances (50kg): €10.00-€50.00 per unit
Professional IT equipment: €2.00-€8.00 per unit
Administrative and WEEE Compliance Costs
PoM declaration preparation and submission: €500-€2,000 annually per country
Reporting and WEEE compliance documentation: €1,000-€5,000 annually
Compliance software or management systems: €2,000-€10,000 annually
Legal and consulting fees for WEEE compliance: €3,000-€15,000+ annually
Take-Back and Collection Infrastructure
Establishing collection points and reverse logistics for electrical and electronic waste management
Varies significantly by manufacturer's WEEE compliance approach
Range: €5,000-€100,000+ annually depending on scale
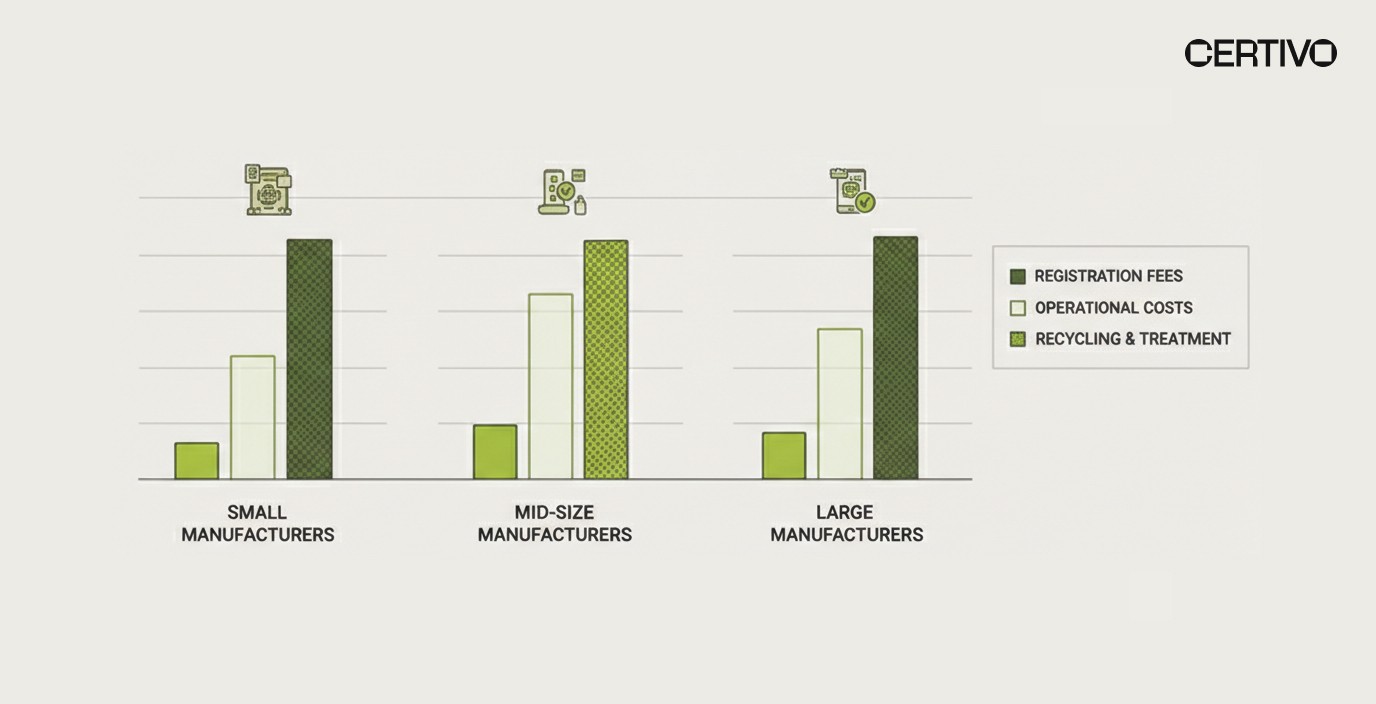
Total Cost Scenarios for WEEE Compliance
Small Manufacturer (10,000 units annually, EU only) - WEEE Compliance Budget:
Registration/membership: €3,000
Eco-contributions (average €0.50/unit): €5,000
Administrative: €2,000
Total WEEE Compliance Cost: ~€10,000 annually
Mid-Size Manufacturer (100,000 units, 5 EU countries) - WEEE Compliance Estimate:
Registration/membership (5 countries): €15,000
Eco-contributions: €30,000-€50,000
Administrative: €10,000
Total WEEE Compliance Cost: ~€55,000-€75,000 annually
Large Global Manufacturer (1,000,000+ units, 15+ countries) - Enterprise WEEE Compliance:
Registration/membership (15+ countries): €50,000-€100,000
Eco-contributions: €500,000-€1,000,000+
Administrative/consulting: €50,000-€200,000
Total WEEE Compliance Cost: €600,000-€1,300,000+ annually
For enterprises operating at this scale, Certivo's guide on cost savings through proactive compliance with AI outlines how automation reduces administrative overhead and prevents costly reporting errors across multiple jurisdictions.
Cost Reduction Strategies for Optimizing WEEE Compliance
Product Design Optimization
Reduce product weight where functionally feasible
Use materials with lower recycling complexity affecting WEEE compliance fees
Design for disassembly to improve material recovery rates
Potential savings: 10-20% of eco-contribution fees
Collective Compliance Schemes
Join group schemes rather than operating individual systems
Share infrastructure costs across multiple manufacturers
Reduced administrative overhead for WEEE compliance management
Potential savings: 20-30% vs. individual compliance operations
Take-Back Coordination
Coordinate collection with other manufacturers
Share transportation and consolidation infrastructure
Establish regional collection hubs reducing WEEE compliance costs
Potential savings: 15-25%
Digital Compliance Platforms
Implement software solutions for automated reporting
Reduce manual data entry and associated errors
Enable real-time WEEE compliance tracking
Potential savings: 10-15% on administrative costs
The most effective digital compliance platforms integrate EPR reporting software capabilities directly into existing ERP and PLM systems—creating an integrated compliance thread that auto-populates PoM declarations, calculates eco-contributions by jurisdiction, and generates audit-ready WEEE reporting outputs without manual intervention.
Registration and Reporting Obligations for WEEE Compliance
Step-by-Step Registration Process for Achieving WEEE Compliance
Step 1: Identify Applicable Countries for WEEE Compliance
Determine all EU member states where products will be sold
Consider countries where distributors will place electrical and electronic equipment on market
Account for future market expansion in WEEE compliance planning
Step 2: Register for WEEE Compliance with National Authority
Contact designated registration body (typically environmental ministry)
Compile required documentation:
Company registration and tax identification
Product descriptions and technical specifications
Product category classifications (WEEE categories 1-10)
Estimated annual quantities of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE)
Proof of financial provision for WEEE compliance
Step 3: Provide Annual PoM Declarations
At start of each calendar year, declare prior year's electrical and electronic waste quantities
Format specified by each national authority (typically online portal)
Include:
Quantity of products placed on market (in units)
Total weight of electrical and electronic equipment (in kg)
Product category distribution
Corrections or updates to prior declarations
Step 4: Pay Associated Fees
Registration fees (annual WEEE compliance renewal)
Eco-contributions based on PoM quantities
Payment typically due by specified deadline (April 30 in many countries)
Late payment penalties: 5-10% surcharge plus interest
PoM Declaration Accuracy and WEEE Compliance Integrity
Definition: "Placing on the Market" means making electrical and electronic equipment available for the first time on the market, whether manufactured locally or imported.
What Counts as PoM:
Products manufactured and sold directly
Products imported for resale
Products supplied to distributors within territory
Products supplied to retailers within territory
Accuracy Critical for WEEE Compliance:
Under-declaring creates legal liability and potential fraud charges
Audits frequently focus on PoM accuracy—companies face substantial fines for misrepresentation
Best practice: Use point-of-sale data and shipping records to substantiate declarations
Annual Reporting Requirements for Ongoing WEEE Compliance
Collection Data Reporting:
Quantity of electrical and electronic waste collected
Weight of collected materials
Delivery dates and collection facility information
Reporting frequency: Annually for WEEE compliance assurance
Recycling/Recovery Reporting:
Percentage of electrical and electronic waste materials recovered
Breakdown by material category (metals, plastics, glass)
Hazardous substance removal and treatment
Reuse vs. recycling split
Reporting requirement: Annually, typically by end of February
Streamlined WEEE reporting is essential for manufacturers operating across multiple EU jurisdictions. Purpose-built EPR reporting software consolidates PoM data, collection volumes, and recycling rates into a single platform—eliminating the spreadsheet fragmentation that causes missed deadlines and inaccurate filings. For more on replacing manual processes, see Certivo's guide on building a future-ready compliance infrastructure.
Treatment, De-Pollution, and Recycling Requirements for WEEE Compliance
Authorized Treatment Facilities and De-Pollution Processes
Collected electrical and electronic waste cannot be disposed of in landfills. Products must be transported to Authorized Treatment Facilities where specialized de-pollution and recovery processes occur as part of WEEE compliance operations.
Critical De-Pollution Requirements for WEEE Compliance:
CFC/HCFC Removal: Refrigerators and some appliances contain ozone-depleting refrigerants requiring separate capture and destruction
PCB Removal: Transformers and capacitors containing polychlorinated biphenyls require specialist extraction
Mercury Removal: Lighting products and displays contain mercury requiring careful removal
Battery Extraction: All batteries must be removed and treated separately
Asbestos Handling: Older electrical and electronic equipment may contain asbestos
Other Hazardous Components: Oil, lead, cadmium, and other hazardous materials must be isolated
The de-pollution process underscores why specialized substance reporting solutions matter—manufacturers must document exactly which hazardous materials are present in each product category to ensure treatment facilities apply the correct extraction protocols. This level of material traceability begins with thorough BOM-level data upstream in the supply chain.
Compliance Mechanisms - Individual vs. Collective Schemes
Individual Compliance Systems vs. Collective Schemes
Individual Compliance Systems for WEEE Compliance:
Definition: Manufacturer establishes and operates its own WEEE compliance system independently, without joining collective schemes.
Requirements:
Establish separate registration in each country for WEEE compliance
Establish individual collection and treatment infrastructure
Fund all collection, transportation, and recycling independently
Submit individual PoM declarations and collection reports
Maintain separate WEEE compliance documentation
Cost Structure:
Individual WEEE compliance typically 40-60% more expensive than collective schemes
Higher infrastructure costs (collection centers, logistics, staff)
Higher administrative overhead for maintaining WEEE compliance
Economies of scale only achieved at very high volumes
Collective Compliance Schemes:
Definition: Multiple manufacturers collectively establish WEEE compliance systems through shared infrastructure, typically operated by third-party administrator.
Advantages:
Significantly lower costs through shared infrastructure (40-60% savings vs. individual WEEE compliance)
Established collection network immediately available
Reduced administrative burden for WEEE compliance management
Geographic coverage across entire country/region
Better positioned to meet collection targets ensuring ongoing WEEE compliance
Whether operating through individual systems or a collective WEEE compliance scheme, manufacturers must ensure their chosen mechanism delivers continuous audit-ready documentation—maintaining verifiable records of registrations, PoM declarations, fee payments, and treatment certificates that can withstand regulatory scrutiny at any time.
Non-Compliance Risks and Penalties
Financial Penalties Across Jurisdictions
European Union Member States - WEEE Compliance Penalties:
Registration failure: €5,000-€50,000 per country
PoM declaration falsification: €10,000-€500,000
Failure to meet collection obligations: €10,000-€100,000+ per year shortfall
Improper treatment documentation: €5,000-€50,000
United Kingdom - WEEE Compliance Enforcement:
Registration/compliance scheme non-membership: Up to £50,000 fine
PoM reporting failures: Up to £50,000 fine per offense
Environmental Agency prosecution: Unlimited fines for serious breaches
Restrictions on product distribution and sales
Germany (Particularly Strict WEEE Compliance Enforcement):
Registration failures: €1,000-€5,000 per month
PoM falsification: €300,000+ criminal and civil penalties
Treatment violations: €5,000-€50,000 per incident
Business Consequences Beyond Financial Penalties
Supply Chain Disruption:
Retailers and distributors may suspend orders due to WEEE compliance concerns
Product sales may be blocked at borders
Distribution agreements cancelled
Reputational Damage:
Public disclosure of non-compliance in regulatory databases
Media coverage of significant WEEE compliance violations
Customer loss due to sustainability concerns
To understand how compliance failures cascade into broader supply chain risk, see Certivo's analysis on why ESG failure is a supply chain risk, not just a reporting issue.
Best Practices for WEEE Compliance Management
Comprehensive WEEE Compliance Management Framework
Compliance Assessment and WEEE Compliance Strategy
Conduct comprehensive WEEE compliance audit across all markets
Identify all applicable WEEE compliance requirements by product and geography
Establish baseline compliance status and identify gaps
Develop risk mitigation strategy addressing highest-risk areas
How to Achieve Sustained WEEE Compliance
Implement robust product classification system
Establish regular PoM declaration review and approval processes
Conduct quarterly collection infrastructure audits
Maintain comprehensive WEEE compliance documentation
Treatment Partner Management for WEEE Compliance
Establish formal audit protocols for treatment facility partners
Regular site visits verifying proper de-pollution processes
Monitoring of environmental compliance and certifications
Contingency planning for treatment capacity disruptions
Digital Compliance Solutions for WEEE Compliance
Automated PoM declaration preparation from sales data
Real-time WEEE compliance status dashboard
Regulatory requirement database updated for new regulations
Document management with audit trail functionality
The most effective digital compliance solutions go beyond basic reporting—they provide an integrated PLM-ERP compliance thread that connects product data, sales volumes, and regulatory requirements in a single system, ensuring that every PoM declaration and eco-contribution calculation is automatically derived from verified operational data.
How to Achieve Continuous WEEE Compliance Improvement
Developing Your WEEE Compliance Strategy
The answer to ‘How to achieve WEEE compliance’ extends beyond initial registration and basic reporting. Certivo helps you with that. Sustainable WEEE compliance requires strategic optimization:
Strategic Optimization for WEEE Compliance:
Analyze collection performance data to identify regional gaps
Evaluate compliance costs and identify reduction opportunities
Benchmark against industry standards and best performers
Implement continuous improvement initiatives
Invest in circular economy principles, reducing long-term WEEE compliance costs
Advanced WEEE Compliance Strategies:
Develop take-back programs exceeding minimum requirements
Create producer-led collection initiatives in underserved markets
Implement design-for-recycling principles reducing end-of-life complexity
Establish transparency programs communicating WEEE compliance commitment
Partner with environmental organizations amplifying sustainability credentials
For manufacturers managing WEEE alongside RoHS and REACH obligations, Certivo's RoHS and REACH compliance lessons and action steps guide provides a complementary roadmap for harmonizing substance compliance across frameworks.
Future Trends and Regulatory Evolution
Emerging WEEE Compliance Requirements
Extended Product Categories:
Continued expansion of WEEE scope to include previously unregulated categories
Growing regulatory expectations for electrical and electronic waste management
Likely future expansion affecting manufacturers' WEEE compliance obligations
Increased Collection and WEEE Compliance Targets:
Trend toward higher collection rates (85-90% by 2030)
Strengthened enforcement mechanisms and penalties
Expectation of manufacturer-funded expanded collection infrastructure
Design for Recycling and WEEE Compliance Integration:
Regulations increasingly mandate product design considerations for end-of-life
Requirements for modular design facilitating easier electrical and electronic waste recovery
Restrictions on mixed materials and composite structures difficult to separate
Digital WEEE Compliance and Reporting Evolution:
Shift toward automated, real-time WEEE compliance reporting
Blockchain technology for supply chain transparency
AI-powered anomaly detection in compliance data
Integration with broader sustainability and ESG reporting frameworks
Emerging EU requirements around digital product passports and traceability IDs will further transform WEEE compliance, requiring manufacturers to embed machine-readable product data covering material composition, recyclability, and hazardous substance content—extending traceability from production through end-of-life treatment.
Certivo provides complete WEEE compliance solutions using its AI agent CORA. Explore our features today.
Conclusion
WEEE compliance regulatory framework continues to evolve with increasingly stringent WEEE compliance requirements, higher collection targets, and expanded product categories.
For organizations navigating the WEEE regulatory framework, comprehensive WEEE compliance management solutions and expert guidance transform complex requirements into manageable, optimizable operational processes. This guide provides the strategic foundation for achieving sustainable WEEE compliance that protects your business while advancing environmental objectives.
Book a demo today at Certivo and achieve efficient and seamless WEEE compliance in no time.
Lavanya
Lavanya is an accomplished Product Compliance Engineer with over four years of expertise in global environmental and regulatory frameworks, including REACH, RoHS, Proposition 65, POPs, TSCA, PFAS, CMRT, FMD, and IMDS. A graduate in Chemical Engineering from the KLE Institute, she combines strong technical knowledge with practical compliance management skills across diverse and complex product portfolios.
She has extensive experience in product compliance engineering, ensuring that materials, components, and finished goods consistently meet evolving international regulatory requirements. Her expertise spans BOM analysis, material risk assessments, supplier declaration management, and test report validation to guarantee conformity. Lavanya also plays a key role in design-for-compliance initiatives, guiding engineering teams on regulatory considerations early in the product lifecycle to reduce risks and streamline market access.
Her contributions further extend to compliance documentation, certification readiness, and preparation of customer deliverables, ensuring transparency and accuracy for global stakeholders. She is adept at leveraging compliance tools and databases to efficiently track regulatory changes and implement proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Recognized for her attention to detail, regulatory foresight, and collaborative approach, Lavanya contributes significantly to maintaining product compliance, safeguarding brand integrity, and advancing sustainability goals within dynamic, globally integrated manufacturing environments.

