Lavanya
Feb 3, 2026
The UK Health and Safety Executive is advancing one of the most significant chemical restrictions affecting fire safety operations across Great Britain. The proposed UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance framework targets thousands of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances through a group-based approach, eliminating the largest source of PFAS emissions into UK groundwater and soil. With the public consultation closing February 18, 2026, organizations holding firefighting foam inventories face immediate strategic decisions.
This restriction follows the HSE's determination that PFAS-containing firefighting foams represent unacceptable environmental and health risks. Unlike previous substance-by-substance approaches, the group-based methodology prevents manufacturers from simply substituting one harmful PFAS compound for another. Organizations without robust regulatory horizon scanning intelligence capabilities risk missing critical transition deadlines that vary significantly based on facility type and operational risk profile.
Table of Contents
Understanding the UK REACH PFAS Firefighting Foam Restriction
Staggered Phase-Out Timeline and Key Deadlines
Industries and Facilities Facing Direct Compliance Impact
Business and Operational Implications
UK and EU Regulatory Divergence Considerations
Strategic Preparation Checklist
How AI Transforms PFAS Compliance Management
Understanding the UK REACH PFAS Firefighting Foam Restriction
The UK Health and Safety Executive has developed an Annex 15 Restriction Dossier targeting all PFAS in firefighting foams across England, Scotland, and Wales. This comprehensive proposal addresses the environmental persistence that has earned these substances the "forever chemicals" designation, recognizing that PFAS accumulation in ecosystems poses long-term risks that incremental restrictions cannot adequately address.
The HSE UK REACH Public Consultation on PFAS in Firefighting Foams provides the authoritative regulatory framework for this restriction. The consultation period offers industry stakeholders final opportunity to submit technical evidence, socio-economic data, and documentation of transition challenges before HSE delivers its final opinion.
The group-based approach represents a significant departure from traditional chemical regulation methodology. Rather than identifying and restricting individual PFAS compounds, the framework captures the entire substance class based on shared characteristics contributing to environmental persistence. This methodology prevents the regulatory cycling that occurs when manufacturers replace restricted substances with chemically similar alternatives that present comparable risks.
UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance affects organizations differently based on their operational profiles, existing foam inventories, and facility risk classifications. Understanding where your organization falls within the phase-out timeline determines the urgency of transition planning and capital allocation decisions. Proactive compliance risk management becomes essential as the regulatory framework moves toward formal adoption.
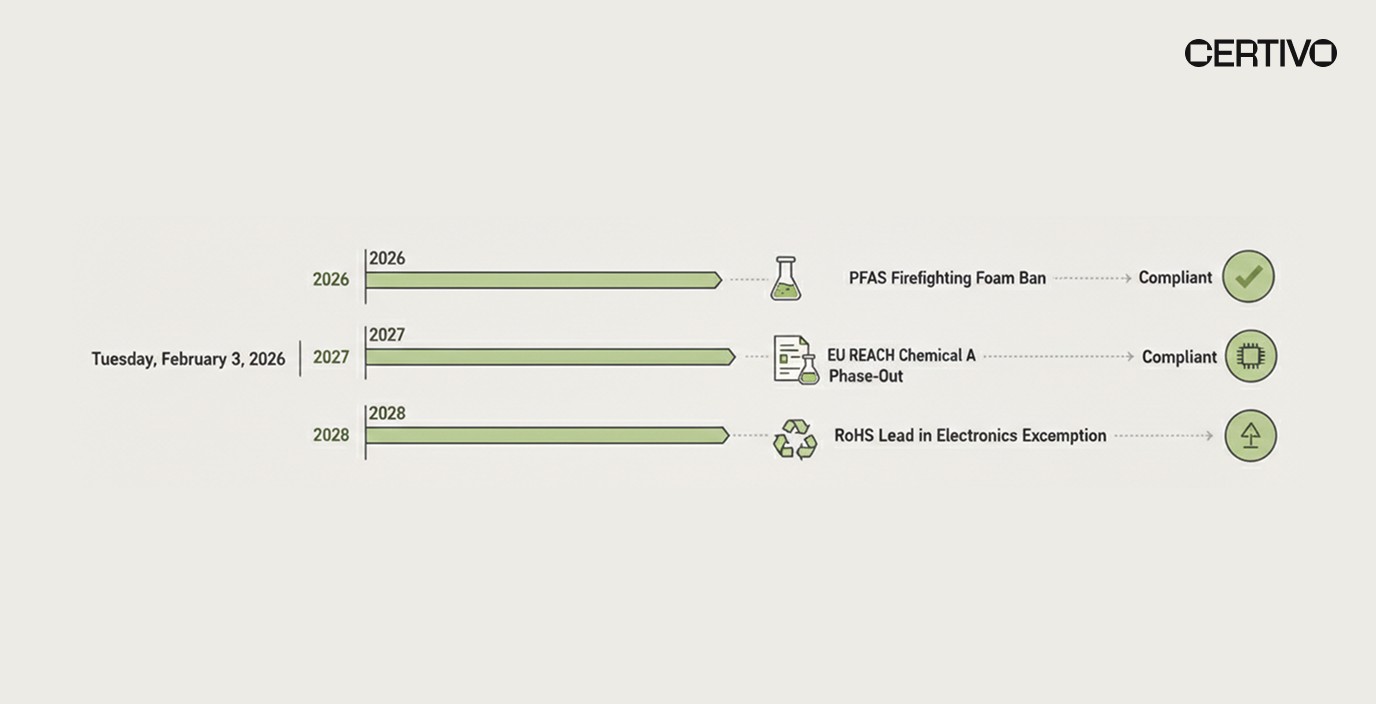
Staggered Phase-Out Timeline and Key Deadlines
The proposed restriction establishes differentiated transition periods recognizing that firefighting foam replacement involves significant operational and capital considerations. Organizations must identify which timeline applies to their operations and plan accordingly.
February 18, 2026: Consultation Deadline
This date marks the final window for industry stakeholders to submit technical evidence and transition challenge documentation. Organizations with unique circumstances or technical barriers should engage with the consultation process before this deadline closes. Input submitted during consultation may influence final transition timeline determinations.
6-Month Transition: Portable Extinguishers
The shortest transition period applies to PFAS-containing portable fire extinguishers. Following formal restriction adoption, manufacturers face a 6-month prohibition on placing new PFAS-containing portable extinguishers on the UK market. This aggressive timeline reflects the availability of fluorine-free foam transition alternatives for portable applications.
5-Year Transition: General Firefighting Applications
Most training activities and municipal firefighting operations face a 5-year transition period for eliminating PFAS foam use. This timeline provides adequate opportunity for:
Equipment assessment and replacement planning
Fluorine-free foam testing and qualification
Operational procedure updates
Personnel training on new foam systems
10-Year Transition: High-Risk Facilities
Extended transition periods apply to high-risk sites including COMAH-regulated petrochemical plants and offshore platforms. The 10-year timeline acknowledges that these facilities require substantial equipment redesign and face unique fire suppression challenges where premature transition could compromise safety.
Transition Period | Affected Applications | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
6 Months | Portable extinguishers | Market placement prohibition |
5 Years | Training and municipal firefighting | General use ban |
10 Years | COMAH sites, offshore platforms | Equipment redesign allowance |
Late 2026 / Early 2027: Expected Formal Adoption
Following consultation review, HSE will deliver final opinion and the formal restriction is expected to enter UK law in late 2026 or early 2027. Organizations should not wait for formal adoption to begin transition planning, as lead times for equipment procurement and foam qualification may exceed available transition periods.
Industries and Facilities Facing Direct Compliance Impact
The PFAS firefighting foam restriction UK framework affects organizations across multiple sectors based on firefighting foam inventory holdings and operational fire suppression requirements.
Petrochemical and Chemical Manufacturing
COMAH-regulated facilities face the most complex UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance obligations. These high-risk sites benefit from extended 10-year transition periods but must begin planning immediately given the magnitude of equipment and procedural changes required. Petrochemical operations typically maintain substantial Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF) stockpiles that require managed disposal.
Industrial automation operations with significant fire risk profiles should evaluate current foam inventories against transition timeline requirements and begin fluorine-free foam qualification testing.
Offshore Oil and Gas Platforms
Offshore platforms present unique challenges for forever chemicals firefighting ban compliance. Remote locations, limited storage capacity, and critical fire suppression requirements complicate transition planning. The 10-year timeline reflects these challenges but organizations should begin supplier qualification and equipment assessment now.
Municipal Fire Services
Fire services across England, Scotland, and Wales face the 5-year general transition timeline. Municipal operations must coordinate foam replacement across multiple stations, vehicles, and equipment types while maintaining operational readiness throughout the transition period.
Aviation and Transportation
Airport firefighting operations relying on AFFF for crash response face compliance obligations under the general 5-year timeline unless classified as high-risk facilities warranting extended transition. The aviation sector has been actively developing fluorine-free alternatives, providing established transition pathways.
Industrial Manufacturing
Manufacturing facilities with onsite fire suppression systems face varying compliance timelines based on risk classification and foam system configurations. Organizations should assess whether their operations fall under general or extended transition provisions. Manufacturing compliance automation helps facilities track requirements across multiple regulatory frameworks.
Business and Operational Implications
UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance creates substantial business consequences extending beyond direct regulatory obligations. Executive leadership must understand these implications to secure appropriate budget allocation and coordinate effectively across operational functions.
Stockpile Management and Disposal Liabilities
Facilities holding AFFF stocks face significant disposal obligations. PFAS-containing foams require decommissioning and disposal through licensed hazardous waste contractors, creating costs that organizations must plan for regardless of whether foam has reached end of useful life. AFFF disposal compliance requirements include:
Proper characterization and documentation of foam inventory
Engagement with licensed hazardous waste contractors
Secure storage pending disposal to prevent environmental release
Documentation maintaining continuous audit-ready compliance records
Organizations maintaining substantial AFFF inventories should begin disposal planning immediately rather than accumulating larger stockpiles requiring eventual elimination. Streamlined supplier documentation processes help track disposal contractor qualifications and waste manifests.
Capital Expenditure Requirements
The fluorine-free foam transition requirements extend beyond simple foam replacement. Different viscosity profiles between PFAS-based and fluorine-free foams often necessitate equipment modifications including:
Storage tank replacement or modification
Pump system upgrades for different flow characteristics
Nozzle and delivery system replacements
Proportioning equipment recalibration or replacement
These capital requirements vary significantly based on existing system configurations. Organizations should commission engineering assessments to develop accurate capital planning estimates before transition deadlines compress available implementation time.
Operational Continuity Considerations
Fire suppression capability must be maintained throughout the transition period. Organizations cannot simply remove PFAS foams without qualified alternatives in place. Transition planning must sequence equipment modifications, foam replacement, and personnel training to maintain continuous fire protection coverage.
Insurance and Liability Implications
Insurance carriers increasingly scrutinize PFAS exposure across policyholder operations. Organizations demonstrating proactive UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance positioning may benefit from more favorable insurance terms, while those delaying transition face potential coverage limitations or premium increases.
UK and EU Regulatory Divergence Considerations
Companies operating in both the UK and EU markets face additional complexity from regulatory divergence between UK REACH and EU REACH frameworks. The broader EU PFAS restriction proposal follows different timelines and may establish different transition periods, creating multi-tier supply chain transparency challenges for organizations managing compliance across jurisdictions.
Timeline Differences
EU PFAS restrictions under development may establish different effective dates and transition periods than the UK framework. Organizations must track both regulatory trajectories to avoid assuming UK compliance satisfies EU requirements or vice versa.
Substance Scope Variations
While both frameworks target PFAS broadly, specific substance definitions and exemption provisions may differ. Products compliant under one framework may require modification for the other market.
Documentation and Reporting Divergence
Different reporting requirements and documentation standards between UK and EU REACH create administrative burden for organizations maintaining market access in both jurisdictions. AI compliance software PFAS monitoring capabilities help organizations track divergent requirements without duplicating compliance infrastructure.
Organizations with cross-border operations should establish compliance monitoring systems capable of tracking both UK and EU regulatory developments. Regulatory change monitoring capabilities prove essential for maintaining awareness as both frameworks evolve.
Strategic Preparation Checklist
Organizations should implement systematic preparation activities to achieve UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance within applicable transition timelines. The following checklist provides framework for compliance program development.
Inventory Assessment and Classification
Document all PFAS-containing firefighting foam inventory by type, quantity, and location
Classify facilities by risk profile to determine applicable transition timeline
Identify foam systems requiring equipment modification for fluorine-free alternatives
Assess disposal requirements and engage licensed hazardous waste contractors
Fluorine-Free Alternative Evaluation
Research available fluorine-free foam alternatives for your specific applications
Conduct compatibility testing with existing equipment
Evaluate performance characteristics against fire suppression requirements
Qualify suppliers and establish procurement relationships
Procurement and supply chain leaders should begin supplier qualification processes for fluorine-free alternatives before demand increases compress lead times.
Capital Planning and Budget Allocation
Commission engineering assessments for equipment modification requirements
Develop capital expenditure estimates for transition implementation
Establish budget allocation across applicable fiscal periods
Identify potential financing or leasing options for equipment replacement
Operational Transition Planning
Develop sequenced transition plans maintaining fire protection continuity
Establish training programs for personnel on new foam systems
Update operational procedures and emergency response protocols
Create contingency plans addressing potential transition complications
Documentation and Compliance Tracking
Implement systems for tracking transition progress against regulatory timelines
Establish continuous audit-ready documentation for disposal activities
Create reporting frameworks demonstrating compliance progress
Document consultation submissions and regulatory engagement
Building future-ready compliance infrastructure during preparation phases establishes foundations for ongoing compliance rather than one-time project completion.
How AI Transforms PFAS Compliance Management
Manual compliance approaches cannot scale to address the complexity of UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance across organizations with multiple facilities, varying risk classifications, and extensive foam inventories. AI compliance software PFAS monitoring capabilities fundamentally transform organizational compliance management.
Automated Regulatory Monitoring
PFAS regulatory landscapes evolve continuously across UK, EU, and other jurisdictions. Automated regulatory monitoring chemicals capabilities track developments across relevant markets, alerting compliance teams to changes requiring response. This regulatory horizon scanning intelligence ensures organizations detect timeline modifications, scope expansions, or exemption changes that affect compliance strategies.
Understanding why people-only compliance cannot scale helps executives appreciate the strategic value of AI-powered monitoring operating continuously across regulatory domains.
Inventory and Transition Tracking
AI platforms enable systematic tracking of foam inventories, disposal activities, and transition progress across multiple facilities. Rather than maintaining disconnected spreadsheets, organizations gain unified visibility into firefighting foam stockpile management across their operations.
Certivo's platform incorporates CORA, an intelligent assistant that automates supplier follow-ups and data collection workflows. For PFAS compliance, CORA can systematically engage fluorine-free foam suppliers, disposal contractors, and equipment vendors to collect documentation required for transition planning and compliance demonstration.
Multi-Jurisdictional Compliance Coordination
Organizations operating across UK and EU markets require compliance systems capable of tracking divergent regulatory requirements simultaneously. AI platforms map products and operations against applicable requirements in each jurisdiction, identifying where compliance activities must differ and where unified approaches suffice.
Global PFAS regulations compliance guidance provides frameworks for managing PFAS compliance beyond UK-specific requirements.
Continuous Audit-Ready Documentation
Compliance documentation must demonstrate transition progress and ongoing compliance with applicable requirements. AI platforms maintain continuous audit-ready documentation that evolves as regulations change and transition activities progress. Staying audit-ready across frameworks becomes systematic practice rather than pre-inspection scramble.
Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for UK PFAS Firefighting Foam Compliance
The UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance framework represents a comprehensive restructuring of fire suppression practices across Great Britain. The group-based restriction approach targeting thousands of forever chemicals simultaneously prevents substitution circumvention while establishing clear transition pathways for affected organizations.
The staggered phase-out timeline, ranging from 6 months for portable extinguishers to 10 years for COMAH-regulated facilities, provides differentiated transition periods reflecting operational complexity. However, organizations should not interpret extended timelines as permission to delay. Capital expenditure requirements, equipment lead times, and fluorine-free foam qualification processes demand immediate planning regardless of applicable transition deadline.
The February 18, 2026 consultation deadline offers final opportunity for stakeholder input before HSE delivers its opinion and formal restriction adoption proceeds. Organizations with unique circumstances should engage with the consultation process while simultaneously advancing internal transition preparations.
Business implications extend beyond regulatory compliance to encompass AFFF disposal compliance requirements, capital expenditure for equipment modification, and insurance considerations that reward proactive positioning. Organizations demonstrating systematic UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance progress gain competitive advantages as enforcement begins.
For companies operating in both UK and EU markets, regulatory divergence creates additional complexity requiring sophisticated compliance monitoring capabilities. AI compliance software PFAS monitoring platforms provide the automated regulatory tracking, inventory management, and documentation capabilities that manual processes cannot deliver at scale.
Executive leadership must recognize that PFAS firefighting foam restriction UK compliance represents operational transformation rather than incremental adjustment. Building robust compliance infrastructure today positions organizations to navigate transition periods successfully while competitors struggle with compressed timelines and inadequate preparation.
Explore how Certivo's AI-powered compliance platform can help your organization manage UK REACH PFAS firefighting foam compliance, track regulatory developments across jurisdictions, and maintain continuous audit-ready documentation throughout the transition period.
Lavanya
Lavanya is an accomplished Product Compliance Engineer with over four years of expertise in global environmental and regulatory frameworks, including REACH, RoHS, Proposition 65, POPs, TSCA, PFAS, CMRT, FMD, and IMDS. A graduate in Chemical Engineering from the KLE Institute, she combines strong technical knowledge with practical compliance management skills across diverse and complex product portfolios.
She has extensive experience in product compliance engineering, ensuring that materials, components, and finished goods consistently meet evolving international regulatory requirements. Her expertise spans BOM analysis, material risk assessments, supplier declaration management, and test report validation to guarantee conformity. Lavanya also plays a key role in design-for-compliance initiatives, guiding engineering teams on regulatory considerations early in the product lifecycle to reduce risks and streamline market access.
Her contributions further extend to compliance documentation, certification readiness, and preparation of customer deliverables, ensuring transparency and accuracy for global stakeholders. She is adept at leveraging compliance tools and databases to efficiently track regulatory changes and implement proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Recognized for her attention to detail, regulatory foresight, and collaborative approach, Lavanya contributes significantly to maintaining product compliance, safeguarding brand integrity, and advancing sustainability goals within dynamic, globally integrated manufacturing environments.

