Lavanya
Feb 3, 2026
The European Chemicals Agency launched a public consultation on February 2, 2026, recommending four hazardous substances for inclusion in the REACH Annex XIV Authorisation List. This regulatory action creates immediate REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance obligations for manufacturers across plastics, electronics, automotive, and packaging sectors who rely on these UV stabilizers, flame retardants, and photoinitiators in their production processes.
Once substances move from the SVHC Candidate List to Annex XIV, companies cannot place them on the market or use them after designated sunset dates without specific authorisation from the European Commission. The authorisation process represents a complex, multi-year endeavor costing hundreds of thousands of Euros with no approval guarantee. Organizations without regulatory horizon scanning intelligence capabilities risk being caught unprepared as these restrictions take effect, potentially facing supply chain disruptions that competitors with proactive compliance programs avoid.
Table of Contents
Understanding the REACH Annex XIV Authorisation Framework
Four Substances Under ECHA Consultation
Key Deadlines and Regulatory Timeline
Industries Facing Direct Compliance Impact
Supply Chain and Business Implications
Compliance Risks and Strategic Considerations
Strategic Preparation Checklist
How AI Transforms REACH Authorisation Compliance
Understanding the REACH Annex XIV Authorisation Framework
The REACH Authorisation List represents the European Union's most restrictive mechanism for controlling hazardous chemical substances. Unlike the SVHC Candidate List, which primarily triggers communication and notification requirements, Annex XIV inclusion effectively bans substance use unless companies secure specific authorisation demonstrating that risks are adequately controlled or socio-economic benefits outweigh risks.
The ECHA Press Release ECHA/NR/26/05 documents the current consultation details. ECHA is seeking stakeholder input on current use volumes, supply chain complexity, potential exemptions for research or medicinal uses, and socio-economic impacts of potential bans.
REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance requires understanding that the authorisation process differs fundamentally from registration or notification procedures. Companies must demonstrate either adequate risk control through exposure management or that socio-economic benefits justify continued use despite risks. This burden of proof shifts regulatory dynamics significantly compared to other chemical management frameworks.
The primary goal of Annex XIV inclusion is forcing chemical substitution toward safer alternatives. ECHA explicitly designs this mechanism to drive innovation and market transformation rather than simply managing ongoing use. Organizations relying on affected substances must begin evaluating alternatives immediately, regardless of final consultation outcomes. Understanding REACH framework requirements provides foundation for comprehensive compliance planning.
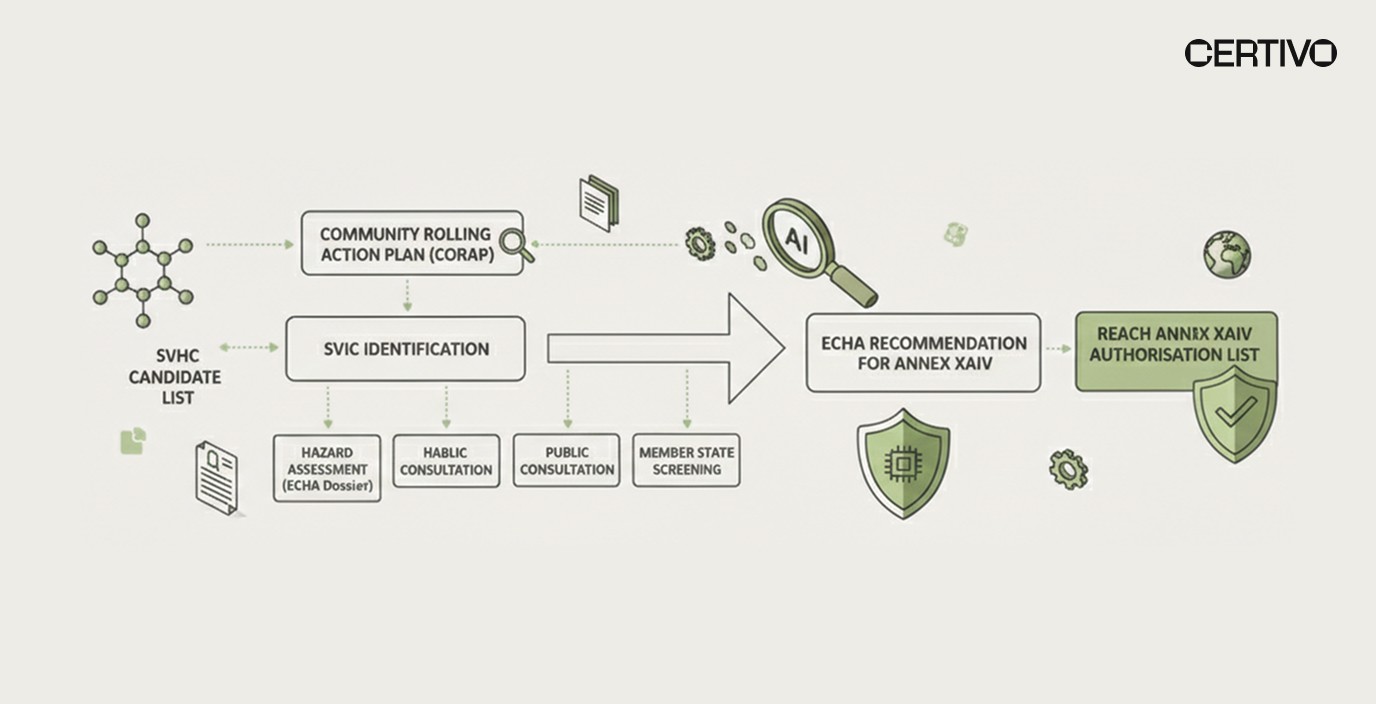
Four Substances Under ECHA Consultation
ECHA's draft recommendation targets four substances with significant industrial applications across multiple sectors. Understanding each substance's characteristics and uses enables targeted compliance responses and BOM-level compliance intelligence for affected product lines.
Impacted Substances and Common Industrial Uses
Substance Name | EC Number | CAS Number | Industrial Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
Bumetrizole (UV-326) | 223-445-4 | 3896-11-5 | UV stabilizer in PVC, polyolefins, and polyesters |
Octrizole (UV-329) | 221-573-5 | 3147-75-9 | UV stabilizer in transparent plastics and food packaging |
Triphenyl Phosphate | 204-112-2 | 115-86-6 | Flame retardant in electronics; plasticizer in adhesives/sealants |
Photoinitiator 379 | 438-340-0 | 119344-86-4 | Curing agent in UV-inks, coatings, and photoresists |
Bumetrizole (UV-326)
This UV stabilizer protects PVC, polyolefins, and polyesters from ultraviolet degradation. UV stabilizer compliance regulations affect manufacturers producing outdoor products, automotive components, and construction materials requiring long-term UV resistance. The substance's widespread use in polymer formulations creates extensive supply chain exposure.
Octrizole (UV-329)
Octrizole serves as a UV stabilizer in transparent plastics and food packaging applications. Its presence in food-contact materials elevates compliance significance given consumer safety implications. Organizations in packaging sectors must evaluate alternative stabilization technologies that maintain optical clarity while meeting REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance requirements.
Triphenyl Phosphate
This flame retardant finds extensive use in electronics and electrical equipment while also functioning as a plasticizer in adhesives and sealants. Flame retardant REACH restrictions affect manufacturers across consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and industrial equipment sectors. The dual functionality as flame retardant and plasticizer complicates substitution efforts. Electronics industry compliance requires particular attention to this substance.
Photoinitiator 379
Used as a curing agent in UV-inks, coatings, and photoresists, this substance affects printing, coating, and semiconductor manufacturing operations. The specialized nature of photoinitiator applications may limit available alternatives, making early substitution research particularly critical.
Key Deadlines and Regulatory Timeline
The REACH Annex XIV authorisation process follows a defined timeline that organizations must track to maintain compliance and business continuity. Understanding these milestones enables proactive preparation rather than reactive scrambling.
February 2, 2026: Public Consultation Launch
ECHA officially launched the public consultation on its draft recommendation. This date marks implementation of the formal consultation process, triggering the comment period during which stakeholders can submit data and perspectives.
May 2, 2026: Public Consultation Closes
Organizations wishing to influence the final recommendation must submit comments by this deadline. ECHA specifically seeks data on:
Current use volumes and supply chain complexity
Potential exemptions for research or medicinal uses
Socio-economic impacts of potential bans
Compliance and regulation managers should coordinate consultation response preparation across affected business units.
Late 2026: Member State Committee Opinion
Following consultation closure, the Member State Committee (MSC) prepares its final opinion on the recommendation. This opinion carries significant weight in the European Commission's ultimate decision.
2027/2028: European Commission Final Decision
The European Commission issues the final decision on Annex XIV inclusion. If substances are added, sunset dates typically take effect 36-48 months after the decision, establishing the deadline after which unauthorised use becomes prohibited.
Projected Sunset Dates: 2030-2032
Based on typical timelines, organizations should anticipate sunset dates falling between 2030 and 2032 for substances added through this consultation process. This timeline provides limited opportunity for chemical substitution requirements EU compliance given the complexity of reformulating established products.
Industries Facing Direct Compliance Impact
REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance creates varying obligations across industries based on substance usage patterns and product characteristics. Executive leadership should evaluate organizational exposure within the following sector categories.
Plastics and Polymers Manufacturing
Plastics manufacturers face significant exposure through UV stabilizer compliance regulations affecting Bumetrizole and Octrizole usage. These substances protect polymer products from UV degradation, and their removal requires identification of alternative stabilization chemistries that maintain product performance.
The widespread use of these stabilizers across PVC, polyolefins, and polyesters creates extensive reformulation requirements. **Building future-ready compliance infrastructure** enables systematic tracking of affected products and reformulation progress.
Electronics and Electrical Equipment
Electronics manufacturers face flame retardant REACH restrictions through Triphenyl Phosphate usage in circuit boards, housings, and components. The substance's dual role as flame retardant and plasticizer complicates replacement, as alternatives must address both functional requirements.
The semiconductor and PCB industry requires particular attention to Photoinitiator 379 usage in photoresist applications critical to chip manufacturing processes.
Automotive and Aerospace
Automotive manufacturers use affected substances in interior components, exterior trim, and electronic systems. UV stabilizers protect dashboard materials and exterior plastics, while flame retardants ensure safety compliance for interior materials.
The automotive industry compliance framework must incorporate REACH authorisation requirements alongside existing safety and environmental regulations.
Packaging and Consumer Goods
Food packaging manufacturers face immediate concern regarding Octrizole usage in transparent packaging materials. Consumer safety implications elevate regulatory scrutiny while limiting acceptable alternatives to those meeting food-contact material requirements.
Construction and Textiles
Construction materials requiring UV stability face reformulation requirements affecting long-term product performance warranties. Textile applications using flame retardants must identify alternatives meeting fire safety standards.
Printing and Inks
Printing operations using UV-curable inks face Photoinitiator 379 restrictions affecting production capabilities. The specialized nature of photoinitiator chemistry may require significant process modifications.
Supply Chain and Business Implications
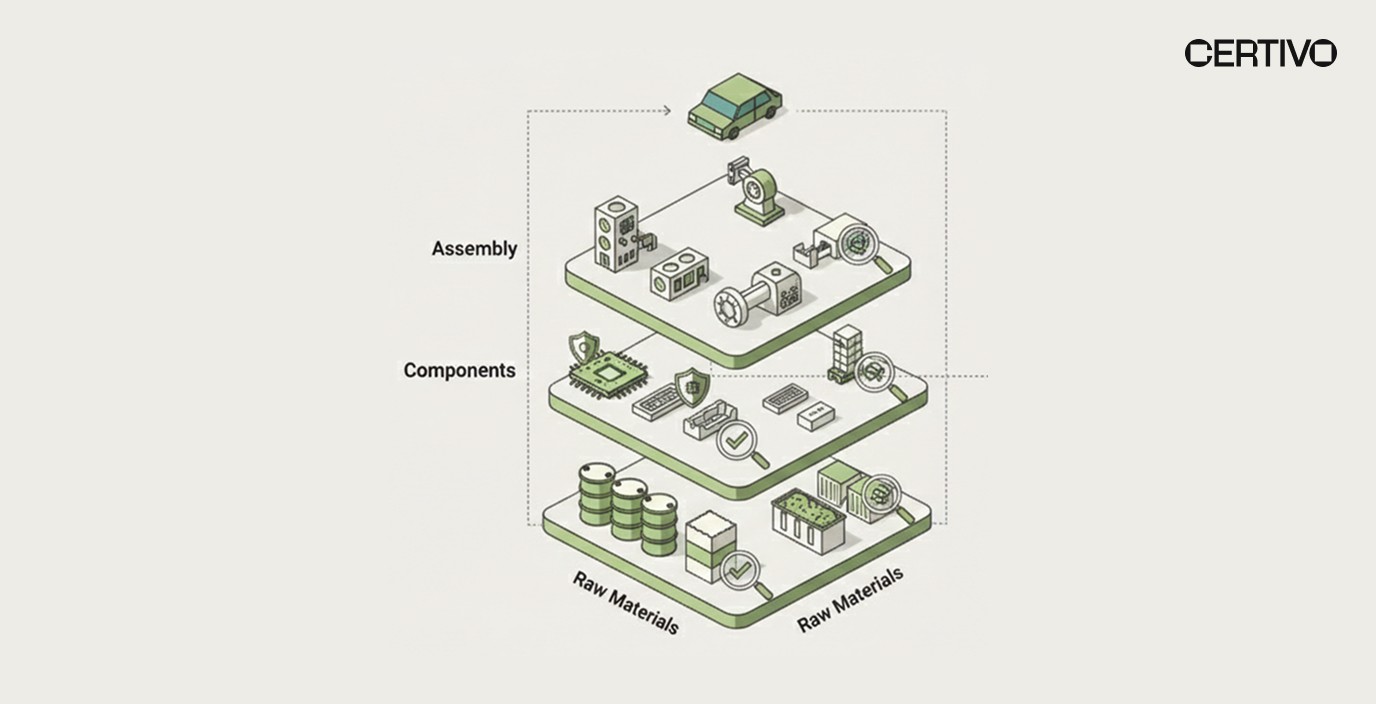
REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance creates business consequences extending beyond direct regulatory obligations. Organizations must understand multi-tier supply chain transparency requirements and commercial implications to secure executive support for compliance investments.
Supply Chain Obsolescence Risk
Even organizations not directly using affected substances face supply chain obsolescence risk. Suppliers may choose to discontinue materials rather than pursue authorisation, creating unexpected supply disruptions for downstream users. This dynamic affects companies throughout value chains, not merely direct substance users.
Effective supplier collaboration becomes critical for identifying supply chain exposure and developing contingency plans before disruptions occur.
Cost of Authorisation Process
Applying for REACH authorisation represents a complex, multi-year process costing hundreds of thousands of Euros with no guarantee of approval. Organizations must weigh authorisation costs against substitution investments when developing compliance strategies.
The authorisation application requires:
Detailed chemical safety assessments
Analysis of alternatives evaluation
Socio-economic impact analysis
Substitution planning documentation
Substitution Investment Requirements
Chemical substitution requirements EU compliance demands R&D investment in alternative formulations. Organizations must validate that alternatives meet performance specifications, manufacturing compatibility, and regulatory requirements across all markets.
AI tools for compliance management help organizations track substitution progress across product portfolios while maintaining continuous audit-ready documentation.
Market Access Considerations
Products containing unauthorised substances after sunset dates cannot be placed on EU markets. Organizations dependent on European revenue must achieve compliance or accept market exclusion. This binary outcome elevates compliance priority for EU-dependent manufacturers.
Compliance Risks and Strategic Considerations
REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance failures carry significant consequences that organizations must understand when evaluating compliance investment priorities.
Market Withdrawal Requirements
Products containing unauthorised substances after sunset dates face mandatory market withdrawal. Unlike temporary supply disruptions, this represents permanent market exclusion absent successful authorisation or reformulation.
Enforcement Actions
Member state authorities enforce REACH requirements through market surveillance and compliance verification. Organizations placing non-compliant products on markets face enforcement actions including fines, product seizures, and reputational damage.
Customer Relationship Impacts
Enterprise customers increasingly require SVHC candidate list substances disclosure and compliance verification. Organizations unable to demonstrate REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance risk losing customer relationships to compliant competitors.
Understanding why compliance teams should drive innovation rather than merely checking boxes helps organizations recognize compliance as competitive advantage rather than cost burden.
Investor and Stakeholder Scrutiny
Investors evaluating manufacturing companies increasingly assess regulatory compliance risk exposure. Organizations with significant SVHC exposure without clear substitution strategies face valuation pressure and capital access challenges.
Strategic Preparation Checklist
Organizations should implement systematic preparation activities to achieve and maintain REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance. The following checklist provides framework for compliance program development.
Product Portfolio Assessment
Identify all products containing affected substances
Map substance usage across formulations and components
Evaluate criticality of each substance to product performance
Prioritize products by revenue exposure and reformulation complexity
Supply Chain Mapping
Survey suppliers regarding substance usage in supplied materials
Identify multi-tier supply chain exposure through component tracking
Assess supplier substitution capabilities and timelines
Develop contingency sourcing strategies for critical materials
Streamlined supplier documentation processes ensure comprehensive supply chain visibility.
Substitution Research
Evaluate available alternative chemistries for each substance
Assess alternative performance against product specifications
Validate regulatory acceptability of alternatives in target markets
Develop reformulation timelines aligned with sunset date projections
Consultation Participation
Compile use volume and supply chain complexity data
Document socio-economic impacts of potential restrictions
Identify exemption applicability for specific applications
Submit consultation comments before May 2, 2026 deadline
Documentation Systems
Implement BOM-level compliance intelligence tracking
Establish continuous audit-ready documentation protocols
Create regulatory change monitoring workflows
Develop enforcement response procedures
Replacing spreadsheets with scalable systems enables systematic compliance management across extensive product portfolios.
How AI Transforms REACH Authorisation Compliance
Manual compliance approaches cannot scale to address the complexity of REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance across extensive product portfolios and global supply chains. AI compliance software chemicals management fundamentally transforms organizational capabilities for regulatory monitoring, substance tracking, and documentation maintenance.
Regulatory Horizon Scanning Intelligence
REACH regulatory landscapes evolve continuously as ECHA advances substances through SVHC identification, candidate list inclusion, and authorisation recommendation processes. Automated regulatory monitoring REACH capabilities track these developments across relevant substances, alerting compliance teams to changes requiring response.
Understanding why people-only compliance cannot scale helps executives appreciate strategic value of AI-powered monitoring operating continuously across regulatory domains.
BOM-Level Substance Tracking
Product portfolios containing thousands of components require systematic screening against SVHC candidate list substances and authorisation requirements. AI platforms enable automated screening that identifies affected products within hours rather than weeks of manual review.
Tracking compliance by BOM provides granular visibility into substance presence across product structures.
Multi-Tier Supply Chain Transparency
Supply chain compliance automation extends organizational visibility beyond direct suppliers to encompass upstream material sources where substance exposure may originate. AI platforms automate supplier data collection, verify substance declarations, and flag gaps requiring remediation.
Certivo's platform incorporates CORA, an intelligent assistant that automates supplier follow-ups and data completion workflows. Rather than manual email chasing, CORA systematically engages suppliers to collect required substance information, reducing administrative burden while improving data completeness.
Continuous Audit-Ready Documentation
Compliance documentation must demonstrate current substance status and substitution progress throughout authorisation timelines. AI platforms maintain continuous audit-ready documentation that evolves as regulatory requirements change and substitution efforts advance.
Staying audit-ready across frameworks becomes systematic compliance practice rather than episodic scramble.
Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for REACH Authorisation Readiness
ECHA's recommendation to move four substances to the REACH Annex XIV Authorisation List signals significant compliance obligations approaching for manufacturers across plastics, electronics, automotive, packaging, and printing sectors. Bumetrizole, Octrizole, Triphenyl Phosphate, and Photoinitiator 379 serve critical functions in numerous industrial applications, and their potential authorisation requirement demands immediate strategic response.
The REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance pathway requires organizations to choose between costly authorisation applications, chemical substitution investments, or market exit. The consultation period closing May 2, 2026, provides opportunity to influence final recommendations, while the projected 2030-2032 sunset dates establish timelines for complete compliance achievement.
Supply chain obsolescence risk affects organizations throughout value chains, not merely direct substance users. Suppliers may discontinue materials rather than pursue authorisation, creating unexpected disruptions for unprepared downstream users. Multi-tier supply chain transparency becomes essential for identifying and mitigating this exposure.
The complexity of managing REACH Annex XIV authorisation compliance across multiple substances, extensive product portfolios, and global supply chains exceeds what manual processes can reliably manage. AI compliance software chemicals management provides the regulatory monitoring, substance tracking, and documentation capabilities that sustainable compliance requires.
Executive leadership must recognize that chemical substitution requirements EU compliance represents ongoing operational reality rather than one-time project. Organizations building robust compliance infrastructure today position themselves to address not only current authorisation recommendations but continuing evolution of REACH restrictions affecting their industries.
Explore how Certivo supports REACH compliance readiness to assess your organization's exposure to evolving authorisation requirements and develop AI-powered strategies ensuring EU market access while reducing compliance operational burden.
Lavanya
Lavanya is an accomplished Product Compliance Engineer with over four years of expertise in global environmental and regulatory frameworks, including REACH, RoHS, Proposition 65, POPs, TSCA, PFAS, CMRT, FMD, and IMDS. A graduate in Chemical Engineering from the KLE Institute, she combines strong technical knowledge with practical compliance management skills across diverse and complex product portfolios.
She has extensive experience in product compliance engineering, ensuring that materials, components, and finished goods consistently meet evolving international regulatory requirements. Her expertise spans BOM analysis, material risk assessments, supplier declaration management, and test report validation to guarantee conformity. Lavanya also plays a key role in design-for-compliance initiatives, guiding engineering teams on regulatory considerations early in the product lifecycle to reduce risks and streamline market access.
Her contributions further extend to compliance documentation, certification readiness, and preparation of customer deliverables, ensuring transparency and accuracy for global stakeholders. She is adept at leveraging compliance tools and databases to efficiently track regulatory changes and implement proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Recognized for her attention to detail, regulatory foresight, and collaborative approach, Lavanya contributes significantly to maintaining product compliance, safeguarding brand integrity, and advancing sustainability goals within dynamic, globally integrated manufacturing environments.

