Hari Prasanth
Jan 26, 2026
Table of Contents
Why Electronics Supply Chain Compliance Defines Market Access in 2026
The Multi-Tier Supplier Compliance Challenge
Regulatory Frameworks Driving Electronics Compliance Complexity
Why Manual Compliance Processes Fail at Electronics Scale
The True Cost of Electronics Compliance Failures
How AI-Powered Compliance Automation Solves Multi-Tier Challenges
BOM-Level Compliance Intelligence: The Electronics Game-Changer
Real-Time Supplier Risk Scoring and Automated Onboarding
Building Market-Ready Electronics Supply Chains
What Electronics Leaders Must Do Now
1. Why Electronics Supply Chain Compliance Defines Market Access in 2026
Electronics supply chain compliance has evolved from a back-office documentation exercise to a strategic imperative that directly determines which manufacturers can access lucrative global markets and which face systematic exclusion. In 2026, electronics companies confronting REACH substance restrictions, RoHS material prohibitions, conflict minerals transparency mandates, PFAS reporting obligations, and Extended Producer Responsibility requirements discover that multi-tier supplier compliance determines competitive positioning as decisively as product innovation or manufacturing efficiency.
The fundamental challenge: electronics manufacturers bear ultimate regulatory responsibility for products incorporating thousands of components sourced through complex global supply chains extending three to five tiers deep, yet most organizations lack visibility beyond tier-one contract manufacturers and direct component suppliers. This supply chain opacity creates compliance gaps where manufacturers certify regulatory compliance to customers and authorities based on incomplete, unverified, or entirely missing upstream data—exposing organizations to enforcement actions, product recalls, customs detention, and customer disqualification regardless of good-faith compliance efforts.
For electronics manufacturers, the stakes are existential. European Union market access requires REACH SVHC declarations and RoHS compliance for every component in products ranging from smartphones to industrial controls. U.S. federal contracts demand conflict minerals due diligence demonstrating responsible sourcing through multi-tier supply chains. Asian markets impose jurisdiction-specific substance restrictions and certification requirements that vary by country and product category. The result: a compliance matrix of overwhelming complexity where a single component failure cascades through entire product lines, delaying launches and excluding products from critical markets while competitors with AI compliance platforms maintain uninterrupted market access.
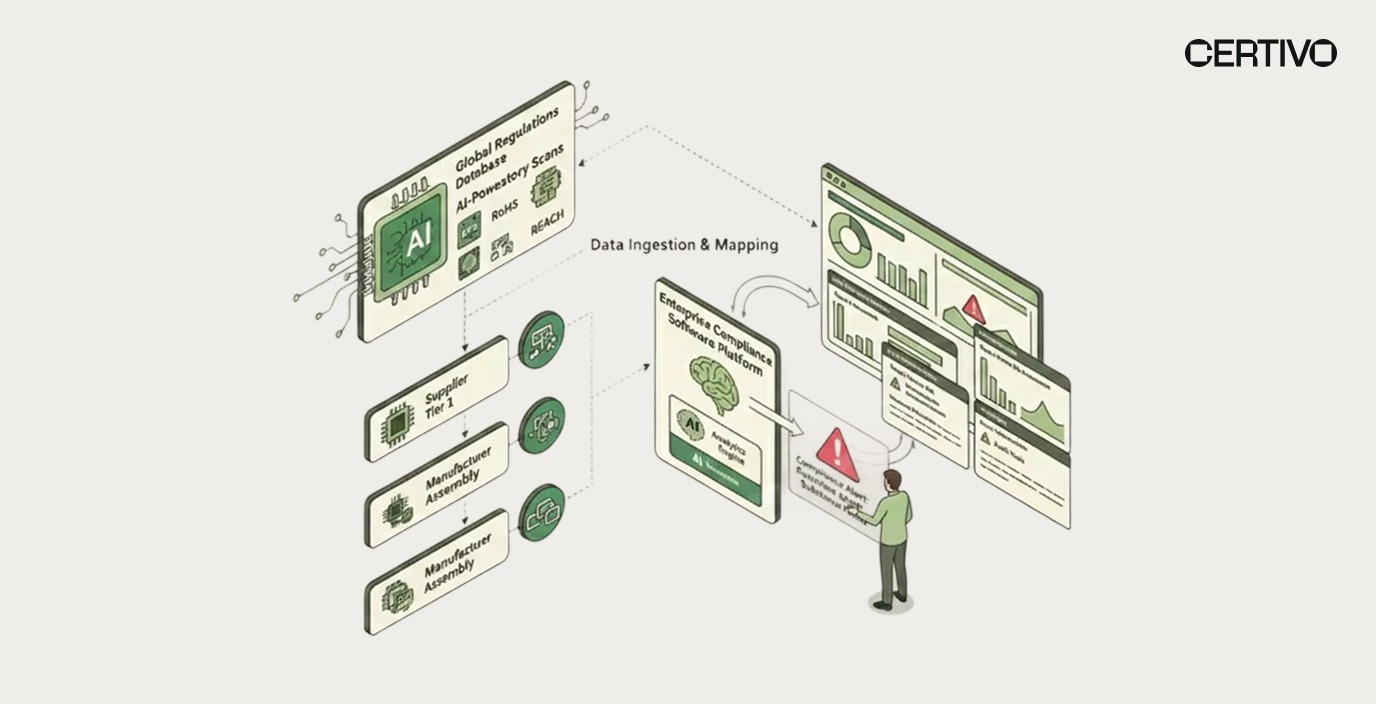
The convergence of regulatory expansion and supply chain complexity creates three defining crises for 2026 electronics compliance: regulatory velocity exceeding organizational adaptation capacity, supply chain opacity preventing reliable verification, and enforcement intensity creating immediate financial consequences for compliance failures. Organizations treating compliance as periodic documentation exercises rather than continuous operational capabilities will find themselves systematically excluded from major markets as regulatory requirements tighten and enforcement mechanisms intensify across global jurisdictions.
2. The Multi-Tier Supplier Compliance Challenge
Electronics supply chains typically extend three to five tiers deep, with tier-one contract manufacturers sourcing from tier-two component suppliers who purchase from tier-three material suppliers and tier-four raw material producers. Each tier introduces compliance data dependencies where electronics manufacturers bear ultimate responsibility for regulatory compliance without direct visibility into upstream supplier operations, material sourcing decisions, or substance composition at raw material levels.
The Tier-One Data Illusion
Most electronics companies implement multi-tier supplier compliance verification only at tier-one, collecting supplier declarations from contract manufacturers and direct component suppliers while assuming tier-one partners verify their own upstream supply chains. This assumption creates systematic compliance failures because tier-one suppliers typically lack resources, expertise, or motivation to conduct rigorous upstream verification. When regulatory audits or customer inquiries demand supply chain transparency, manufacturers discover tier-one declarations rest on incomplete or unverified upstream data that cannot withstand scrutiny.
The tier-one illusion manifests in scenarios that expose compliance gaps: a contract manufacturer certifies products as RoHS compliant based on component supplier declarations, but those suppliers never verified substance composition with their raw material sources. When testing reveals restricted substances, the manufacturer faces recalls despite possessing "compliant" tier-one certifications. Legal and financial liability remains with the manufacturer while tier-one and tier-two suppliers claim they acted in good faith based on information available to them—leaving manufacturers without recourse and customers without remediation.
Organizations implementing automated supplier data collection capabilities that extend verification through multiple supply chain tiers eliminate the tier-one illusion by systematically engaging upstream suppliers, validating declarations against material composition databases, and maintaining continuous compliance visibility as supplier relationships and component sourcing evolve across complex global networks.
Data Degradation Across Supplier Tiers
Automated compliance verification becomes critical as supplier data quality degrades systematically when information travels upstream through supply chain tiers. Tier-one suppliers may provide detailed declarations for major components, but responses often include qualifiers like "to the best of our knowledge" that shift verification responsibility without providing actionable data. Tier-two component suppliers frequently lack internal systems to track substance composition, responding to compliance inquiries with generic certifications or failure to respond at all. Tier-three material suppliers operate in markets where compliance infrastructure is minimal, making upstream verification practically impossible through traditional supplier engagement alone.
This data degradation creates compliance confidence gaps where electronics manufacturers must certify regulatory compliance to customers and authorities based on incomplete, unverified, or missing upstream data. The gap between regulatory requirements for "due diligence" and actual supply chain visibility exposes manufacturers to enforcement risk regardless of good-faith efforts to collect supplier declarations through conventional methods that cannot scale to multi-tier supplier networks spanning hundreds of organizations across dozens of countries.
The Response Time Problem in Multi-Tier Networks
Multi-tier supply chains create temporal delays preventing rapid compliance response when regulations change or customers demand verification. A regulatory update requiring new substance declarations initiates cascading information requests: manufacturer to tier-one, tier-one to tier-two, tier-two to tier-three, with each tier requiring weeks or months to respond. By the time upstream data reaches manufacturers, regulatory deadlines have passed or customer opportunities have closed—creating market access barriers where compliance speed determines commercial success as decisively as technical capabilities.
The response time problem intensifies as electronics products incorporate more components from diverse suppliers. A smartphone with 1,000+ components from 200+ suppliers across 20+ countries creates compliance response timelines measured in quarters when regulations require response in weeks. Manufacturers must either accept incomplete compliance data, delay product launches while waiting for supplier responses, or invest in compliance automation platforms that eliminate multi-tier data dependencies through intelligent automation, predictive risk assessment, and proactive supplier engagement workflows.
3. Regulatory Frameworks Driving Electronics Compliance Complexity
Electronics manufacturers navigate a regulatory landscape where substance restrictions, supply chain transparency mandates, and environmental compliance frameworks overlap to create compliance obligations that manual processes cannot systematically address across global operations and multi-tier supplier networks spanning dozens of jurisdictions with conflicting requirements and enforcement mechanisms.
REACH: The European Compliance Baseline
The European Union's Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) establishes substance of very high concern (SVHC) disclosure requirements applying to virtually all electronics products sold in EU markets. With the SVHC candidate list exceeding 240 substances and expanding quarterly, electronics manufacturers must verify absence or declare presence of these substances in every component, material, and packaging element across entire product portfolios—creating data assembly challenges that exceed manual compliance capacity.
BOM-level compliance intelligence addresses REACH complexity by automating SVHC tracking at the component level, monitoring regulatory updates in real-time, and triggering compliance workflows when new substances are added to the candidate list. Without automation, manufacturers face impossible data assembly timelines as REACH obligations extend through multi-tier supply chains where component suppliers lack visibility into their own material suppliers' substance composition decisions—creating verification gaps that expose manufacturers to enforcement actions despite substantial compliance investments.
RoHS: Substance Restrictions at Component Level
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive prohibits specific substances in electrical and electronic equipment sold in EU markets, with compliance requiring verification at the component level rather than finished product testing alone. RoHS compliance failures create immediate market access blocks, with customs authorities detaining shipments pending verification and retailers refusing products without valid compliance documentation—resulting in revenue loss, inventory obsolescence, and customer relationship damage that extends beyond immediate financial impacts.
The challenge: RoHS compliance demands substance composition data for every component in complex electronics assemblies, but component suppliers frequently cannot provide required detail without engaging their own material suppliers. Electronics manufacturers must implement automated regulatory compliance for electronics manufacturers systems that systematically extract substance data from suppliers, validate responses against regulatory requirements, and maintain continuous compliance as component sourcing and supplier relationships evolve across dynamic global supply chains.
Conflict Minerals: Supply Chain Transparency Mandates
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission conflict minerals rules require publicly traded electronics companies to conduct due diligence determining whether products contain tin, tantalum, tungsten, or gold sourced from conflict-affected regions. Compliance demands tracing minerals through complex supply chains to smelter or refiner level—requiring engagement with tier-three and tier-four suppliers who may lack incentive or capability to provide required transparency.
Multi-tier supplier data collection platforms enable systematic conflict minerals due diligence by automating smelter identification, engaging upstream suppliers through standardized information requests, and maintaining audit-ready documentation demonstrating reasonable efforts to determine mineral origins. Organizations lacking automated conflict minerals programs face compliance failures not from intentional non-compliance but from inability to assemble required supply chain data within reporting timelines mandated by SEC regulations.
PFAS: Emerging Substance Restrictions
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) restrictions are expanding globally, with states like California and Maine implementing reporting requirements and phase-out mandates for products containing intentionally added PFAS. Electronics manufacturers must assess PFAS presence in components ranging from circuit board coatings to cable insulation, requiring supplier verification across multi-tier supply chains where PFAS may appear in processing aids, surface treatments, or material formulations that suppliers don't routinely disclose.
The PFAS compliance challenge demonstrates why electronics supply chain compliance automation is essential: manufacturers must simultaneously track hundreds of substances across multiple regulatory frameworks while maintaining continuous compliance as regulations expand and enforcement intensifies—creating verification burdens that manual processes cannot sustain without systematic automation and intelligent risk assessment capabilities.
4. Why Manual Compliance Processes Fail at Electronics Scale
Manual compliance processes relying on spreadsheets, email chains, and periodic supplier surveys cannot scale to meet the data volume, verification complexity, and response speed demands of modern electronics supply chain compliance. Organizations attempting manual compliance management discover systematic failures manifesting as data gaps, validation errors, deadline misses, and enforcement exposure that threaten market access and competitive positioning.
Data Volume Overwhelms Manual Tracking
A mid-sized electronics manufacturer managing 500 product SKUs with 5,000 components sourced from 300 suppliers across three supply chain tiers must track compliance status for dozens of substance restrictions across multiple jurisdictions—generating data volumes that spreadsheet-based tracking cannot manage without version control failures, update delays, and accuracy erosion. Each regulatory change triggers cascading supplier engagement requirements: distributing information requests, tracking responses, validating data quality, updating compliance records, and generating reports for customers and authorities.
Manual tracking creates data silos where compliance, procurement, engineering, and quality teams maintain separate spreadsheets with conflicting information. When regulatory audits or customer inquiries demand compliance evidence, organizations discover discrepancies between departmental records that undermine compliance certifications and expose enforcement vulnerabilities. Real-time compliance risk scoring systems eliminate data silos by centralizing compliance information in unified platforms that provide single-source-of-truth visibility accessible to all stakeholders across organizational functions.
Supplier Engagement Cannot Scale Manually
Electronics manufacturers must collect compliance declarations from hundreds of suppliers across multiple tiers, but manual engagement through email requests and follow-up calls cannot scale to supplier network complexity. Suppliers receive compliance inquiries from multiple customers using different templates and requesting overlapping information, creating supplier fatigue that reduces response rates and degrades data quality. Non-responsive suppliers create compliance gaps that manufacturers must address through escalation, alternative sourcing, or acceptance of incomplete data—each option creating operational friction or compliance risk.
Automated supplier data collection platforms standardize supplier engagement through unified portals where suppliers submit declarations once and fulfill multiple customer requirements, reducing supplier burden while improving response rates and data quality. Automation enables systematic supplier follow-up, tracks compliance performance over time, and identifies high-risk suppliers requiring additional verification or replacement—transforming supplier compliance from periodic crisis response to continuous operational capability.
Regulatory Updates Outpace Manual Monitoring
Electronics manufacturers must monitor regulatory developments across dozens of jurisdictions, with substance restrictions, reporting requirements, and enforcement policies changing continuously. Manual monitoring through regulatory websites and industry newsletters creates awareness gaps where organizations discover regulatory changes weeks or months after effective dates—missing compliance deadlines and creating enforcement exposure. When REACH adds new SVHCs or jurisdictions implement PFAS restrictions, manufacturers lacking automated compliance verification capabilities cannot rapidly assess impacts on product portfolios or initiate supplier engagement within compressed timelines.
The regulatory monitoring challenge intensifies as compliance obligations expand globally. A manufacturer selling electronics in EU, U.S., and Asian markets must track REACH, RoHS, conflict minerals, PFAS, and jurisdiction-specific requirements across 20+ countries—creating monitoring burdens that manual processes cannot sustain without dedicated compliance teams whose size exceeds economic viability for most organizations. AI-powered regulatory intelligence platforms automate monitoring, assess regulatory impacts on products, and trigger compliance workflows automatically—enabling lean compliance teams to manage global obligations that would otherwise require staff expansions incompatible with operational efficiency goals.
5. The True Cost of Electronics Compliance Failures
Electronics compliance failures create financial impacts extending far beyond immediate enforcement penalties, with cascading consequences affecting revenue, profitability, market access, customer relationships, and competitive positioning. Organizations underestimating compliance failure costs discover that inadequate compliance infrastructure generates losses measured in millions of dollars annually through mechanisms that compound over time.
Customs Delays and Product Detention
Non-compliant electronics shipments detained at customs create immediate revenue loss as products cannot reach customers within contracted delivery timelines. Customs authorities increasingly scrutinize electronics imports for REACH and RoHS compliance, detaining shipments lacking valid declarations or testing reports. Detention generates costs including storage fees, expedited shipping for replacement products, customer penalties for late delivery, and administrative expenses resolving customs holds—with financial impacts reaching hundreds of thousands of dollars for single incidents affecting high-value electronics shipments.
Beyond immediate costs, customs detention damages customer relationships and creates market access restrictions. Retailers experiencing delivery delays from compliance issues disqualify suppliers from future contracts, closing market access channels that took years to establish. Organizations experiencing repeated customs detention face enhanced scrutiny from authorities, creating permanent compliance barriers where every future shipment receives detailed review—increasing import times and costs indefinitely.
Product Recalls and Market Withdrawals
Compliance failures discovered after products reach markets trigger mandatory recalls that generate costs exponentially higher than initial compliance investments would have required. Electronics recalls for REACH or RoHS violations demand retrieving products from distribution channels, notifying customers, coordinating returns logistics, disposing of non-compliant inventory, and implementing corrective actions proving future compliance—with total costs often exceeding product revenues by substantial margins.
Market withdrawals create secondary impacts including brand reputation damage, lost market share to competitors, and customer relationship impairment that persists long after recall completion. Media coverage of compliance-related recalls amplifies reputational damage, with social media and industry publications broadcasting compliance failures to audiences including customers, investors, and prospective employees—creating stakeholder confidence impacts that extend beyond immediate financial losses.
Customer Disqualification and Contract Loss
Enterprise electronics customers increasingly embed compliance requirements into supplier contracts, with rigorous verification standards and audit rights ensuring suppliers maintain continuous compliance capabilities. Suppliers failing customer compliance audits face contract termination, disqualification from future bidding, and relationship damage extending across customer organizations. For electronics manufacturers deriving significant revenue from major customers, disqualification events create existential threats requiring emergency remediation and relationship repair efforts consuming executive attention and organizational resources.
Customer disqualification ripples through organizations beyond immediate contract loss. Sales teams lose credibility with prospective customers who discover disqualification history through industry networks. Marketing teams struggle positioning organizations as quality suppliers when compliance failures become industry knowledge. Executive teams face board scrutiny regarding compliance management and strategic risk oversight—creating governance challenges that distract from growth initiatives.
Enforcement Actions and Legal Liability
Regulatory authorities enforce electronics compliance requirements through civil penalties, consent decrees, and public enforcement actions creating both financial liability and reputational damage. EU authorities enforce REACH and RoHS violations with penalties reaching hundreds of thousands of euros per violation, with multiple violations creating cumulative liability that threatens organizational viability. U.S. enforcement of conflict minerals and other supply chain transparency requirements carries substantial penalties plus ongoing monitoring and reporting obligations that consume compliance resources indefinitely.
Beyond government enforcement, electronics manufacturers face private litigation from customers, consumers, and advocacy organizations alleging compliance failures. Class action lawsuits for products containing restricted substances create defense costs and settlement obligations potentially exceeding millions of dollars, with litigation consuming executive time and creating investor relations challenges as material legal proceedings require public disclosure. Organizations implementing AI compliance platforms proactively reduce enforcement and litigation risk by maintaining continuous compliance verification and audit-ready documentation demonstrating due diligence efforts.

6. How AI-Powered Compliance Automation Solves Multi-Tier Challenges
Electronics supply chain compliance automation tools leveraging artificial intelligence transform compliance from reactive documentation exercises to proactive operational capabilities that scale across complex global supplier networks while maintaining continuous verification, intelligent risk assessment, and audit-ready documentation. AI-powered platforms address fundamental limitations of manual compliance processes by automating supplier engagement, extracting data from unstructured documents, predicting compliance risks, and adapting to regulatory changes in real-time.
Intelligent Supplier Data Collection at Scale
AI-powered compliance platforms automate supplier engagement through unified portals distributing standardized information requests, tracking response rates, sending automated reminders, and escalating non-responsive suppliers through procurement channels. Natural language processing extracts compliance data from unstructured supplier documents including PDFs, emails, and certificates—eliminating manual data entry that creates transcription errors and consumes staff time. Machine learning algorithms validate supplier declarations against regulatory requirements, flag inconsistencies requiring follow-up, and identify high-risk suppliers based on response patterns and declaration quality.
The automation advantage: organizations implementing automated supplier data collection reduce supplier engagement time from weeks to days while improving response rates and data quality. Suppliers access self-service portals where single declarations fulfill multiple customer requirements, reducing supplier burden and increasing participation. Automated validation catches declaration errors before data enters compliance systems, preventing downstream failures and rework. The result: systematic supplier verification across multi-tier networks at scale and speed impossible through manual processes.
BOM-Level Compliance Intelligence and Risk Scoring
AI platforms analyze bill of materials at component level, mapping substances and regulatory requirements to every part in products ranging from simple assemblies to complex systems with thousands of components. BOM-level compliance intelligence enables proactive risk identification before products enter development, allowing engineering teams to select compliant components and avoid redesign costs from late-stage compliance failures. Compliance scoring algorithms assess product-level risk by analyzing component compliance status, supplier reliability, regulatory change impacts, and historical compliance performance—providing executive dashboards showing compliance status across product portfolios.
Real-time compliance risk scoring systems continuously evaluate compliance posture as components change, suppliers update declarations, and regulations evolve. Risk scores trigger automated workflows: high-risk products receive expedited compliance review, at-risk components generate alternative sourcing recommendations, and regulatory changes automatically assess impacts on affected products. The intelligence layer transforms compliance from backward-looking documentation to forward-looking risk management that prevents failures rather than merely detecting them.
Automated Regulatory Monitoring and Impact Assessment
AI-powered regulatory intelligence platforms monitor global developments across jurisdictions, automatically identifying regulatory changes affecting electronics supply chains. Machine learning algorithms parse regulatory text, extract compliance requirements, and assess impacts on products and components—generating actionable intelligence that manual monitoring cannot provide at comparable speed or comprehensiveness. When REACH adds SVHCs or jurisdictions implement new restrictions, automated systems immediately identify affected products, calculate compliance gaps, and initiate supplier engagement workflows.
The monitoring advantage extends beyond awareness to action: AI compliance platforms don't merely alert teams to regulatory changes but automatically execute compliance workflows addressing changes. Regulatory updates trigger supplier information requests for newly restricted substances, engineering teams receive notifications identifying affected components, and compliance teams access pre-generated action plans outlining verification steps and deadlines. Automation transforms regulatory change from crisis triggers to managed transitions where organizations maintain continuous compliance despite accelerating regulatory velocity.
Integration with ERP and PLM Systems
Modern compliance platforms integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and product lifecycle management (PLM) systems, creating unified data architectures where compliance information flows seamlessly across organizational functions. ERP integration enables compliance status visibility in procurement workflows, preventing purchase orders for non-compliant components. PLM integration embeds compliance requirements in product development processes, ensuring new products incorporate only verified-compliant components. The integration eliminates data silos where compliance, procurement, engineering, and manufacturing teams operate from different information sources creating coordination failures and compliance gaps.
Integration delivers operational efficiency beyond compliance: automated data exchange eliminates duplicate data entry, reduces error rates, and accelerates workflows spanning multiple systems. Compliance status becomes real-time operational intelligence accessible across organizational functions rather than periodic reports distributed after decisions have already been made. Organizations implementing integrated compliance platforms achieve both regulatory assurance and operational excellence as compliance capabilities enhance rather than impede business velocity.
7. BOM-Level Compliance Intelligence: The Electronics Game-Changer
BOM-level compliance intelligence represents the most significant advancement in electronics compliance capabilities, enabling component-level substance tracking, predictive risk assessment, and proactive compliance verification that prevents failures rather than merely detecting them after products reach markets. Organizations implementing BOM-level intelligence transform compliance from documentation burdens to competitive advantages where compliance confidence accelerates product launches and strengthens customer relationships.
Component-Level Substance Tracking
Traditional compliance approaches verify finished products through testing or tier-one supplier declarations, discovering component-level compliance issues only after products enter production or reach markets. BOM-level intelligence tracks substance composition at individual component level, linking every part number to verified substance declarations, regulatory requirements, and supplier compliance performance. When components change or regulations update, systems automatically identify affected products and trigger verification workflows—preventing compliance failures through proactive risk management.
Component-level tracking enables scenario analysis where organizations evaluate compliance impacts of alternative components before making sourcing decisions. Engineering teams compare compliance profiles of equivalent components from multiple suppliers, selecting options that minimize regulatory risk while meeting technical and cost requirements. The capability transforms compliance from design constraint to design enabler where comprehensive substance intelligence expands rather than limits component selection options.
Predictive Compliance Risk Assessment
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical compliance data, supplier performance patterns, regulatory trends, and component characteristics to predict compliance risks before they manifest as violations. Predictive models identify high-risk components requiring additional verification, flag suppliers with declining declaration quality, and anticipate regulatory changes likely to affect specific product categories. Multi-tier supplier compliance platforms leverage predictive intelligence to prioritize verification efforts, allocate compliance resources efficiently, and prevent failures through proactive intervention.
The predictive advantage: organizations move from reactive compliance addressing failures after they occur to proactive compliance preventing failures before they happen. Compliance teams focus resources on highest-risk areas identified by predictive models rather than spreading efforts uniformly across all products and suppliers. Risk-based compliance delivers both better regulatory outcomes and operational efficiency as scarce compliance resources target areas where intervention delivers greatest risk reduction.
Automated Compliance Verification Workflows
BOM-level intelligence platforms automate verification workflows spanning supplier engagement, data validation, risk assessment, and documentation maintenance. When new products enter development, automated workflows verify component compliance, request supplier declarations for unverified parts, and alert engineering teams to high-risk components requiring alternatives. Throughout product lifecycles, continuous monitoring detects changes in component sourcing, supplier declarations, or regulatory requirements—triggering verification workflows maintaining compliance as products evolve.
Workflow automation eliminates manual coordination across compliance, procurement, engineering, and quality teams. Systems automatically route tasks to appropriate stakeholders, track completion status, escalate delayed items, and maintain audit-ready documentation of all verification activities. The automation enables lean compliance teams to manage product portfolios and supplier networks at scale that would otherwise require staff expansions incompatible with organizational efficiency goals.

8. Real-Time Supplier Risk Scoring and Automated Onboarding
Real-time compliance risk scoring systems evaluate supplier performance continuously, analyzing declaration quality, response timeliness, audit findings, and regulatory compliance history to generate supplier risk profiles that inform procurement decisions, vendor onboarding processes, and ongoing supplier management. Organizations implementing supplier risk scoring transform compliance from periodic assessments to continuous intelligence that proactively identifies and remediates supplier risks before they create product compliance failures.
Continuous Supplier Performance Monitoring
AI-powered platforms track supplier compliance performance across multiple dimensions: declaration completeness and accuracy, response time to information requests, audit performance, corrective action implementation, and regulatory violation history. Performance metrics generate composite risk scores updated in real-time as new information becomes available, providing procurement teams with current supplier risk profiles during sourcing decisions. Low-performing suppliers trigger automated workflows: compliance teams receive alerts requiring additional verification, procurement receives recommendations for alternative sourcing, and suppliers receive performance feedback identifying required improvements.
Continuous monitoring replaces periodic supplier audits with ongoing intelligence gathering that detects performance degradation immediately rather than months later during scheduled reviews. Organizations identify supplier compliance issues early when remediation options exist, preventing downstream impacts on product compliance and customer relationships. The continuous approach delivers both better risk management and operational efficiency as automated monitoring eliminates costly on-site audits except for highest-risk situations requiring detailed investigation.
Automated Vendor Onboarding and Qualification
Electronics manufacturers qualifying new suppliers for approved vendor lists must verify compliance capabilities before authorizing component purchases. Manual qualification processes requiring comprehensive documentation review and capability assessments consume weeks or months, delaying procurement decisions and creating supply chain inflexibility. Automated compliance verification platforms accelerate vendor onboarding through standardized qualification workflows collecting required compliance information, validating supplier capabilities, and generating approval recommendations based on objective risk assessment criteria.
Automated onboarding maintains qualification standards while reducing cycle times from weeks to days. Suppliers access self-service portals submitting required documentation and compliance certifications, systems automatically validate submissions against qualification criteria, and compliance teams receive approval recommendations with supporting evidence. The acceleration enables organizations to qualify alternative suppliers rapidly when primary suppliers experience capacity constraints or quality issues, maintaining supply chain resilience without compromising compliance verification rigor.
Supplier Collaboration and Continuous Improvement
Leading compliance platforms facilitate supplier collaboration through portals where suppliers access compliance requirements, submit declarations, receive performance feedback, and participate in continuous improvement initiatives. Transparency regarding compliance expectations and performance standards enables suppliers to proactively address issues rather than reactively responding to customer complaints. Collaboration platforms support supplier capability building through training resources, best practice guidance, and benchmarking data showing performance relative to peer suppliers.
Supplier collaboration transforms adversarial compliance relationships based on audits and corrective actions into partnership approaches where manufacturers and suppliers jointly manage compliance as shared responsibility. Collaborative approaches deliver better compliance outcomes by addressing root causes of supplier non-compliance—typically lack of resources, expertise, or awareness rather than willful non-compliance. Organizations building collaborative supplier compliance capabilities achieve both better regulatory outcomes and stronger supplier relationships that enhance supply chain resilience beyond compliance contexts.
9. Building Market-Ready Electronics Supply Chains
Electronics market readiness compliance verification supplier networks extend beyond regulatory compliance to encompass customer requirements, industry standards, and competitive positioning elements that collectively determine market access and commercial success. Organizations building market-ready supply chains implement compliance capabilities that satisfy regulatory minimums while exceeding customer expectations and establishing competitive differentiation through compliance excellence.
Customer-Specific Compliance Requirements
Enterprise electronics customers increasingly impose compliance requirements exceeding regulatory minimums, demanding supplier certifications for specific substances, conflict minerals programs meeting industry best practices, and audit rights verifying ongoing compliance capabilities. Manufacturers selling to multiple customers must navigate overlapping but non-identical customer requirements creating compliance complexity that manual processes cannot systematically address. Automated regulatory compliance for electronics manufacturers platforms map customer requirements to internal compliance capabilities, identify gaps requiring remediation, and maintain customer-specific compliance documentation enabling rapid response to audit requests and information inquiries.
Meeting customer requirements delivers competitive advantages beyond contract compliance. Suppliers demonstrating compliance excellence through rapid audit response, proactive issue disclosure, and continuous improvement initiatives strengthen customer relationships and gain preferred supplier status. Preferred status translates to commercial benefits including longer contract terms, increased purchase volumes, early involvement in new product development, and resilience when supply chain disruptions force customers to consolidate supplier bases.
Industry Standards and Certification Programs
Electronics industry standards including IPC specifications, automotive quality requirements, and aerospace certification programs impose compliance obligations complementing regulatory requirements. Organizations pursuing industry certifications must demonstrate systematic compliance management capabilities including documented processes, trained personnel, and continuous improvement mechanisms. Compliance platforms supporting industry standards accelerate certification by maintaining audit-ready documentation, tracking corrective actions, and demonstrating compliance management maturity that certification bodies require.
Industry certification delivers market access benefits as customers in regulated industries (automotive, aerospace, medical devices) require supplier certification as contract qualification prerequisites. Certification differentiates suppliers in competitive markets where technical capabilities and pricing have converged, making compliance excellence a decisive competitive factor. Organizations achieving certification gain access to customer segments and market opportunities unavailable to non-certified competitors, justifying compliance infrastructure investments through revenue growth rather than merely cost avoidance.
Competitive Positioning Through Compliance Excellence
Forward-looking electronics manufacturers recognize compliance excellence as competitive differentiator rather than cost center, investing in compliance capabilities that exceed industry norms and customer expectations. Compliance excellence manifests through metrics including rapid regulatory change response, zero customs detention events, consistent customer audit performance, and proactive substance restriction adoption. Organizations achieving compliance excellence strengthen brand reputation, customer confidence, and market positioning—transforming compliance from defensive risk management to offensive competitive strategy.
Competitive positioning through compliance creates sustainable advantages that competitors cannot easily replicate. Building comprehensive supplier networks with verified multi-tier compliance requires years of systematic investment that new market entrants cannot compress through accelerated spending. Organizations establishing compliance leadership positions defend market share while capturing share from competitors experiencing compliance failures that create customer relationship impairment and market access restrictions.
10. What Electronics Leaders Must Do Now
Electronics manufacturers and supply chain executives must act immediately to build compliance capabilities that address 2026 regulatory requirements while positioning organizations for future compliance landscape evolution. Deferring compliance infrastructure investments creates accumulating risks as regulatory requirements tighten, enforcement intensifies, and customer expectations increase—making proactive compliance capability development both regulatory necessity and strategic imperative.
Assess Current Compliance Infrastructure Gaps
Organizations must conduct comprehensive assessments evaluating current compliance capabilities against regulatory requirements and industry best practices. Assessments should identify gaps in supplier data collection, substance tracking, regulatory monitoring, risk assessment, and documentation maintenance. Gap analysis informs investment prioritization, with critical gaps requiring immediate remediation and lower-priority gaps addressed through phased implementation roadmaps. Honest assessment prevents false confidence where organizations believe existing processes provide adequate compliance when systematic gaps create hidden risks.
Implement AI-Powered Compliance Automation
Electronics manufacturers relying on manual compliance processes must transition to AI compliance platforms providing automated supplier engagement, BOM-level intelligence, predictive risk assessment, and continuous regulatory monitoring. Platform implementation should prioritize highest-risk products and suppliers, demonstrating value through quick wins before expanding to complete product portfolios. Organizations implementing AI-powered automation achieve both immediate compliance improvements and long-term capability foundation enabling continuous adaptation as regulatory requirements evolve.
Establish Multi-Tier Supplier Verification Programs
Manufacturers must extend supplier verification beyond tier-one to engage tier-two and tier-three suppliers providing critical components and materials. Multi-tier programs require systematic engagement strategies, standardized information requests, and automated tracking ensuring verification completeness across complex supplier networks. Organizations establishing multi-tier visibility eliminate compliance blind spots where upstream supplier failures cascade into finished product non-compliance despite tier-one verification efforts.
Integrate Compliance with Product Development
Electronics companies must embed compliance requirements in product development processes, ensuring new products incorporate only verified-compliant components and meet regulatory requirements before entering production. Integration requires PLM system connectivity, engineering team training, and design review processes incorporating compliance verification as mandatory milestones. Early-stage compliance integration prevents costly redesign when compliance issues surface late in development cycles—accelerating time-to-market while reducing compliance risk.
Build Continuous Improvement Capabilities
Organizations must establish continuous improvement mechanisms where compliance performance is measured, analyzed, and improved systematically over time. Metrics including supplier response rates, declaration quality, audit findings, and regulatory change response times provide improvement focus areas. Regular reviews engaging cross-functional teams identify process improvements, technology enhancements, and organizational capabilities strengthening compliance maturity. Continuous improvement transforms compliance from static capabilities to dynamic capabilities that evolve with regulatory landscape and business requirements.
Conclusion: Electronics Supply Chain Compliance as Strategic Capability
Electronics supply chain compliance in 2026 determines which manufacturers access lucrative global markets and which face systematic exclusion through enforcement actions, customer disqualification, and competitive disadvantage. Organizations treating compliance as documentation exercises discover that regulatory complexity, supply chain opacity, and enforcement intensity overwhelm manual processes—creating compliance failures that threaten revenue, profitability, and market position.
The solution: electronics supply chain compliance automation tools leveraging AI to automate supplier engagement, track substances at BOM level, score risks in real-time, and adapt to regulatory changes continuously. Organizations implementing automated compliance platforms transform compliance from defensive cost centers to offensive competitive capabilities that accelerate market access, strengthen customer relationships, and establish sustainable competitive advantages.
Electronics leaders must act now to build compliance infrastructure addressing 2026 requirements while positioning organizations for regulatory landscape evolution. Deferring investments creates accumulating risks as requirements tighten and enforcement intensifies—making proactive capability development both regulatory necessity and strategic imperative determining competitive positioning for years to come.
Take Action: Transform Your Electronics Supply Chain Compliance
The complexity of multi-tier supplier compliance demands more than incremental process improvements—it requires fundamental transformation to AI-powered compliance automation that scales across global supplier networks while maintaining continuous verification and intelligent risk management.
Ready to build market-ready electronics supply chains?
Certivo's AI-first compliance platform delivers:
Automated multi-tier supplier data collection eliminating manual engagement bottlenecks
BOM-level compliance intelligence providing component-level substance tracking and risk scoring
Real-time regulatory monitoring automatically assessing impacts on products and suppliers
Integrated compliance workflows connecting procurement, engineering, and compliance teams
Human-in-the-loop expertise combining AI automation with compliance specialist oversight
Discover how leading electronics manufacturers achieve compliance excellence while accelerating time-to-market and reducing operational costs.
Schedule a personalized demo today: https://www.certivo.com/contact
Transform compliance from market access barrier to competitive advantage. Act now to build the compliance infrastructure your organization needs for 2026 and beyond.
Hari Prasanth
Hariprasanth is a Chemical Compliance Specialist with nearly four years of experience, underpinned by a degree in Chemical Engineering. He brings in-depth expertise in global product compliance, working across key regulations such as REACH, RoHS, TSCA, Proposition 65, POPs, FMD, and PFCMRT.
Hari prasanth specializes in reviewing technical documentation, validating supplier inputs, and ensuring that products consistently meet regulatory standards. He works closely with cross-functional teams and suppliers to collect accurate material data and deliver clear, audit-ready compliance reports that stand up to scrutiny.
Through his strong analytical skills and regulatory insight, Hari prasanth enables organizations to navigate evolving compliance challenges while aligning with sustainability initiatives in an increasingly dynamic regulatory environment.

