Lavanya
Jan 30, 2026
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health is finalizing Skin Notation Profiles that will reshape chemical compliance requirements across industries in 2026. Five chemicals, including Allyl Alcohol, Formamide, Formic Acid, Picric Acid, and Phenothiazine, have completed public consultation review and are moving toward formal adoption. This regulatory finalization creates immediate compliance obligations for organizations managing occupational chemical skin exposure risks in workplace environments.
This finalization represents more than routine regulatory updates. NIOSH has fundamentally revised the scientific methodology underlying skin hazard classifications, removing legacy approaches while incorporating advanced dermal absorption modeling. Organizations relying on outdated Safety Data Sheets or manual tracking systems face compliance gaps that AI compliance management for chemical safety platforms can identify and remediate before enforcement intensifies. Proactive compliance risk management becomes essential as these profiles take effect throughout 2026.
Table of Contents
Executive Summary: Why This Matters in 2026
What Are NIOSH Skin Notation Profiles
Scientific and Regulatory Shifts in Finalized Profiles
Chemicals Under Final Review and Their Industrial Significance
Business and Compliance Risks of Dermal Exposure
Industries Facing Direct Compliance Impact
What Compliance and EHS Teams Must Do Now
How AI Transforms Chemical and Occupational Compliance
2026 Compliance Timeline and Implementation Priorities
Executive Summary: Why This Matters in 2026
NIOSH Skin Notation Profiles provide the authoritative scientific foundation for workplace chemical risk assessment AI systems and manual compliance programs alike. With finalization occurring in 2026, organizations must update hazard communications, revise exposure controls, and modify operational procedures across affected facilities. These changes will influence regulatory enforcement, insurance evaluations, and stakeholder expectations throughout the year and beyond.
The five chemicals receiving finalized profiles span multiple industrial applications. Allyl Alcohol appears in pharmaceutical synthesis and plastics manufacturing. Formamide serves as a solvent across laboratory and industrial settings. Formic Acid finds extensive use in textile processing and leather tanning. Picric Acid remains relevant in explosives manufacturing and laboratory analysis. Phenothiazine functions as an antioxidant in petroleum products and pharmaceutical intermediates.
Organizations without AI tools for regulatory compliance capable of tracking these developments risk reactive compliance postures that increase costs, extend timelines, and expose operations to enforcement scrutiny. The 2026 finalization creates urgency for building future-ready compliance infrastructure that addresses skin notation requirements systematically before enforcement actions commence.
What Are NIOSH Skin Notation Profiles
Skin Notation Profiles represent NIOSH's systematic approach to characterizing dermal hazards associated with workplace chemical exposures. These profiles provide scientific rationale for assigning skin hazard notations that inform Safety Data Sheet development, workplace risk assessments, and occupational exposure control strategies across industries handling hazardous substances.
The notation system addresses three primary hazard categories that organizations must understand for effective NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance:
Systemic Toxicity Notations (SYS)
Systemic notations identify chemicals that can be absorbed through skin in quantities sufficient to cause effects beyond the exposure site. The SYS notation indicates potential for systemic toxicity, while SYS (FATAL) designates substances where dermal absorption may produce life-threatening outcomes. These classifications directly influence personal protective equipment requirements and exposure monitoring protocols that compliance teams must implement in 2026.
Direct Skin Effect Notations (DIR)
Direct effect notations characterize localized hazards including irritation and corrosion. DIR indicates general direct effects, DIR (IRR) specifies irritation potential, and DIR (COR) identifies corrosive properties. These classifications drive engineering control requirements and emergency response procedures that compliance and regulation managers must implement across affected operations immediately.
Immune-Mediated Response Notations (SEN)
Sensitization notations identify chemicals capable of triggering immune-mediated reactions following dermal exposure. These classifications carry particular significance for workforce protection, as sensitized workers may experience severe reactions to subsequent exposures at concentrations below standard occupational limits.
Understanding these notation categories enables AI compliance management for chemical safety systems to map regulatory requirements against operational activities and identify gaps requiring remediation as 2026 enforcement expectations intensify.
Scientific and Regulatory Shifts in Finalized Profiles
The 2026 NIOSH finalization introduces methodological changes that compliance teams must understand to maintain NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance. Most significantly, NIOSH has removed the skin-to-inhalation dose (SI) ratio from its assessment framework, reflecting scientific advancements since earlier guidance documents.
Removal of SI Ratio Methodology
Since NIOSH Current Intelligence Bulletin 61 in 2017, dermal absorption science has advanced considerably. The SI ratio, which compared dermal uptake to inhalation exposure, no longer reflects current scientific understanding of skin permeation mechanisms. Finalized profiles eliminate this ratio in favor of more sophisticated dermal absorption modeling approaches that organizations must now incorporate into compliance programs.
This methodological shift affects how organizations interpret existing Safety Data Sheets and workplace risk assessment AI outputs. Documents referencing SI ratios require immediate revision to align with updated scientific frameworks. Automated compliance monitoring for chemicals must account for this transition to prevent compliance gaps as enforcement intensifies throughout 2026.
Enhanced Hazard Characterization Transparency
Finalized profiles provide expanded documentation of the logic underlying notation assignments. This transparency enables compliance teams to understand precisely why specific designations apply, supporting more targeted control measures and more defensible compliance positions during regulatory inquiries.
The ultimate guide to compliance management provides frameworks for incorporating these scientific updates into organizational compliance programs systematically as 2026 requirements take effect.
Chemicals Under Final Review and Their Industrial Significance
The five chemicals receiving finalized Skin Notation Profiles in 2026 represent diverse industrial applications, creating NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance obligations across multiple sectors. Understanding each substance's characteristics and uses enables targeted compliance responses.
Allyl Alcohol (CAS No. 107-18-6)
Allyl Alcohol serves as an intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis, plastics manufacturing, and agricultural chemical production. Its high volatility combined with significant dermal absorption potential creates occupational chemical skin exposure risks that require integrated inhalation and dermal protection strategies. Organizations using Allyl Alcohol in synthesis operations must evaluate current exposure controls against finalized profile recommendations immediately.
Formamide (CAS No. 75-12-7)
Formamide functions as a solvent in pharmaceutical manufacturing, laboratory research, and industrial processes. Reproductive toxicity concerns associated with this substance elevate compliance significance beyond routine skin hazard management. AI tools for regulatory compliance should flag Formamide-containing processes for enhanced monitoring as 2026 enforcement expectations increase.
Formic Acid (CAS No. 64-18-6)
Formic Acid finds extensive industrial application in textile processing, leather tanning, and rubber manufacturing. Its corrosive properties create immediate direct skin effects requiring engineering controls and personal protective equipment. The finalized profile clarifies DIR notation applicability, affecting control requirements across construction and building materials operations using Formic Acid treatments.
Picric Acid (CAS No. 88-89-1)
Picric Acid maintains industrial relevance in explosives manufacturing, laboratory analysis, and certain specialty chemical applications. Its sensitization potential adds SEN notation considerations to systemic and direct effect evaluations. Organizations handling Picric Acid face multi-dimensional occupational chemical skin exposure risks requiring comprehensive control strategies aligned with 2026 requirements.
Phenothiazine (CAS No. 92-84-2)
Phenothiazine serves as an antioxidant in petroleum products and as an intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis. Its photosensitization potential introduces workplace hazard considerations extending beyond standard dermal exposure scenarios. Procurement and supply chain leaders should verify that suppliers provide accurate hazard characterization for Phenothiazine-containing materials reflecting finalized profile requirements.
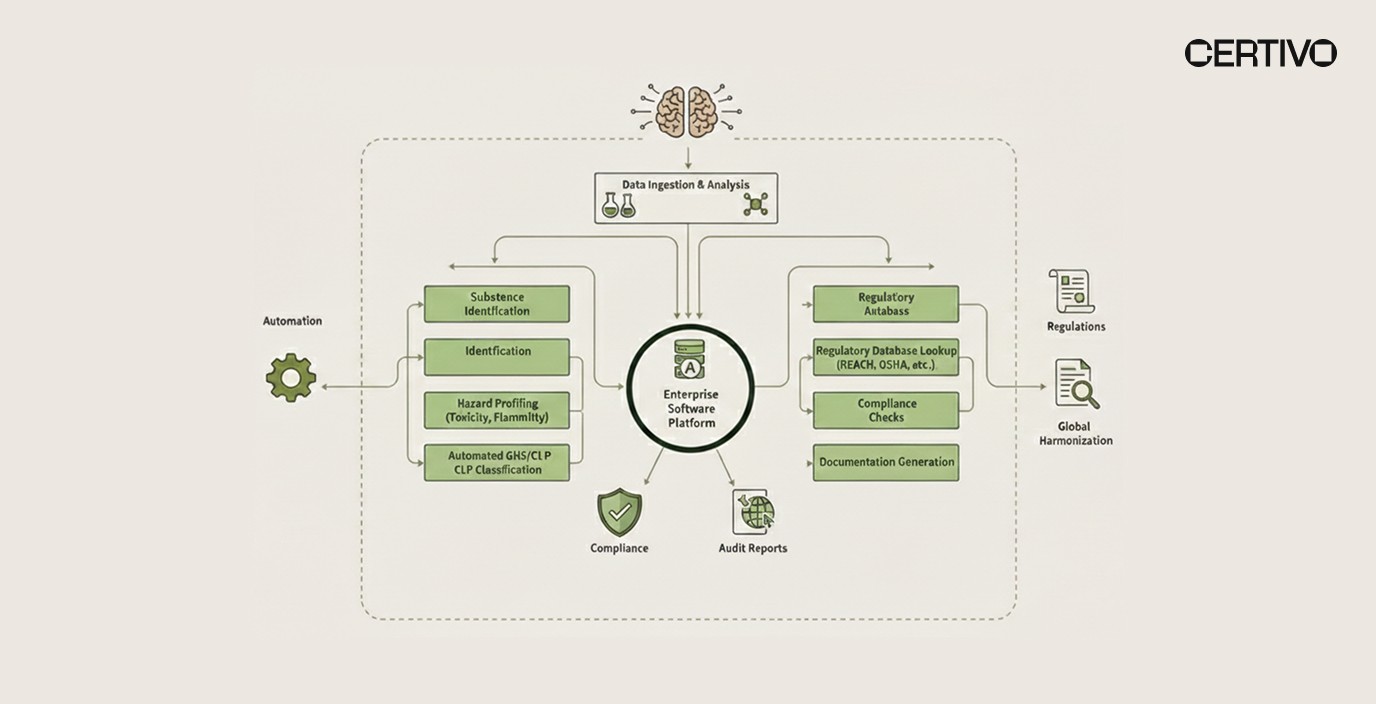
Business and Compliance Risks of Dermal Exposure
Occupational chemical skin exposure risks create business consequences extending beyond immediate worker safety concerns. Organizations must understand these risks to justify AI compliance management for chemical safety investments and secure executive support for compliance program enhancements in 2026.
Regulatory Enforcement Exposure
OSHA enforcement actions increasingly reference NIOSH guidance documents when evaluating workplace hazard controls. Organizations operating with outdated skin hazard assessments face citation risk when inspection findings reveal gaps between 2026 scientific understanding and implemented controls. AI powered EHS compliance software enables proactive identification of these gaps before enforcement scrutiny occurs.
Workers Compensation and Insurance Implications
Skin-related occupational illnesses, including dermatitis, sensitization reactions, and systemic effects from dermal absorption, generate workers compensation claims that affect insurance premiums and self-insured retention costs. Demonstrating compliance with current NIOSH guidance supports favorable insurance evaluations and strengthens defense positions when claims arise. VPs and directors of quality should coordinate with risk management teams to leverage compliance documentation in insurance negotiations.
Supply Chain and Customer Requirements
Enterprise customers increasingly require suppliers to demonstrate occupational safety compliance as a condition of commercial relationships. Organizations unable to document NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance may face commercial disadvantages in competitive procurement processes. **Responding faster to customer RFQs requires compliance documentation systems capable of producing current hazard assessments efficiently.
Workforce Retention and Recruitment
Occupational safety performance affects workforce recruitment and retention, particularly for positions involving chemical handling. Organizations demonstrating commitment to worker protection through current compliance programs gain competitive advantages in labor markets. Automated compliance monitoring for chemicals supports this positioning by ensuring consistent hazard communication and control implementation throughout 2026.
Industries Facing Direct Compliance Impact
The NIOSH finalized Skin Notation Profiles create varying compliance obligations across industries based on chemical usage patterns and workforce exposure scenarios. Executive leadership should evaluate organizational exposure within the following sector categories for 2026 compliance planning.
Chemicals and Chemical Manufacturing
Chemical manufacturers face the most direct NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance obligations in 2026. Organizations producing, processing, or handling the five reviewed substances must evaluate current Safety Data Sheets, exposure assessments, and control measures against finalized profile recommendations. AI compliance management for chemical safety platforms enable systematic review across extensive product portfolios.
Pharmaceuticals and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
Pharmaceutical operations utilizing Allyl Alcohol, Formamide, or Phenothiazine as synthesis intermediates face occupational chemical skin exposure risks requiring integrated controls. The medical devices industry shares similar compliance challenges where chemical intermediates create worker exposure scenarios requiring immediate attention.
Laboratories and Research Institutions
Academic and industrial laboratories maintaining inventories of reviewed substances must update hazard communication materials and exposure control procedures as profiles take effect in 2026. Laboratory operations often involve direct chemical handling that elevates dermal exposure potential compared to automated industrial processes.
Manufacturing and Industrial Processing
Broad manufacturing operations using Formic Acid in processing applications face DIR notation compliance requirements. Industrial automation solutions that reduce worker chemical contact may become more attractive as skin notation requirements clarify control expectations.
Automotive and Transportation
Automotive manufacturing operations utilizing Phenothiazine-containing materials in fuel system components or lubricant formulations must evaluate worker exposure scenarios. The automotive industry compliance framework should incorporate NIOSH skin notation updates alongside existing regulatory requirements for 2026.
Electronics and Electrical Equipment
Electronics manufacturing using solvents containing reviewed substances faces workplace chemical risk assessment AI implementation opportunities. The semiconductor and PCB industry particularly benefits from automated compliance monitoring given complex chemical inventories and evolving regulatory requirements.
What Compliance and EHS Teams Must Do Now
With 2026 finalization underway, compliance teams must act immediately to maintain NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance. Organizations should prioritize the following activities to achieve compliance readiness as enforcement expectations intensify.
Inventory Assessment Against Finalized Substances
Compliance teams must identify where Allyl Alcohol, Formamide, Formic Acid, Picric Acid, and Phenothiazine appear in organizational operations. This assessment should extend beyond primary use to include maintenance chemicals, laboratory reagents, and materials present in supplier-provided formulations. AI tools for regulatory compliance automate this identification across complex inventories efficiently.
Safety Data Sheet Gap Analysis
Current Safety Data Sheets for products containing reviewed substances must be evaluated against finalized profile recommendations. Gaps between existing hazard characterization and final notation assignments indicate areas requiring immediate SDS updates or enhanced exposure controls. Streamlined supplier documentation processes ensure vendors provide current hazard information aligned with 2026 requirements.
Exposure Assessment Revision
Existing workplace exposure assessments require revision to reflect finalized skin notation methodology. The removal of SI ratio approaches affects how historical assessments characterized dermal exposure risks. Workplace chemical risk assessment AI capabilities enable efficient reassessment across multiple exposure scenarios before enforcement actions commence.
Control Measure Verification
Engineering controls, administrative procedures, and personal protective equipment specifications must be verified against finalized profile hazard characterizations. Organizations may identify control upgrades required to address hazard classifications not reflected in current programs. Implementation timelines should align with 2026 enforcement expectations.
Training Program Updates
Worker training programs addressing chemical handling must incorporate finalized skin notation information. Employees handling substances receiving updated profiles need awareness of revised hazard characterizations and any changes to required controls or procedures.
The NIOSH Skin Notation Profiles page provides direct access to finalized documents and supporting technical information for compliance program development.

How AI Transforms Chemical and Occupational Compliance
Manual compliance approaches cannot scale to address the complexity of modern chemical safety requirements. AI compliance management for chemical safety platforms fundamentally change organizational capabilities for monitoring regulatory developments, assessing exposure risks, and maintaining audit-ready documentation throughout 2026 and beyond.
Continuous Regulatory Monitoring
Regulatory landscapes affecting chemical safety evolve continuously across federal, state, and international jurisdictions. AI tools for regulatory compliance provide automated surveillance that identifies relevant developments immediately upon announcement. This capability transforms compliance postures from reactive document chasing to proactive preparation that organizations need as 2026 requirements take effect.
Understanding why people-only compliance cannot scale helps executives appreciate the strategic value of AI-powered monitoring infrastructure that operates continuously across regulatory domains without manual intervention.
Automated Inventory Screening
Chemical inventories spanning thousands of substances require systematic screening against regulatory requirements. Automated compliance monitoring for chemicals enables organizations to identify where regulatory changes affect operations within hours of announcement rather than weeks of manual review. This capability proves particularly valuable when multiple substances receive finalized profiles simultaneously, as occurred with the current NIOSH finalization.
Risk-Based Prioritization
AI powered EHS compliance software enables risk-based prioritization of compliance activities. Rather than treating all regulatory developments equally, AI systems assess organizational exposure and flag high-priority items requiring immediate attention. This capability ensures compliance resources focus on activities generating maximum risk reduction as 2026 enforcement expectations intensify.
Documentation and Audit Readiness
Compliance documentation must demonstrate current practices aligned with applicable requirements. AI systems maintain audit-ready documentation that evolves as regulations change, eliminating the scramble that typically precedes regulatory inspections or customer audits. Staying audit-ready across frameworks becomes systematic rather than episodic with proper AI infrastructure.
Certivo's platform incorporates these AI capabilities within an integrated compliance management environment. CORA, Certivo's intelligent assistant, supports proactive compliance by automating supplier follow-ups, completing data collection workflows, and maintaining documentation currency as regulatory requirements evolve throughout 2026.
2026 Compliance Timeline and Implementation Priorities
With NIOSH Skin Notation Profiles finalization occurring in 2026, organizations must structure compliance activities to achieve readiness before enforcement intensifies. The following implementation framework guides compliance teams through prioritized activities.
Immediate Priority: Assessment and Gap Identification (Q1-Q2 2026)
Organizations should complete inventory assessments, SDS gap analyses, and exposure assessment reviews immediately. This phase establishes baseline understanding of organizational exposure to finalized substances and identifies remediation priorities requiring attention. Replacing spreadsheets with scalable systems accelerates this assessment work significantly.
Near-Term Priority: Control Enhancement and Documentation Update (Q2-Q3 2026)
Following gap identification, organizations must implement control enhancements and documentation updates addressing identified deficiencies. This phase positions organizations for demonstrated compliance when enforcement scrutiny begins rather than scrambling after citations issue.
Ongoing Priority: Verification and Continuous Monitoring (Q3-Q4 2026 and Beyond)
As implementation completes, organizations should verify that measures align with finalized profile content and establish continuous monitoring protocols ensuring ongoing compliance. AI compliance management for chemical safety platforms support this verification and ongoing monitoring seamlessly across the organization.
Stakeholder Communication
CEOs and founders should ensure board-level visibility into NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance preparation. Investor communications should address occupational safety compliance as a risk management priority, demonstrating organizational commitment to worker protection and regulatory alignment throughout 2026.
The ability to standardize compliance across plants and regions ensures consistent implementation regardless of facility location or local management practices as finalized requirements take effect.
Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for Chemical Safety Compliance in 2026
The NIOSH Skin Notation Profiles finalization in 2026 reshapes occupational chemical skin exposure risks management across industries handling hazardous substances. The five chemicals receiving finalized profiles, Allyl Alcohol, Formamide, Formic Acid, Picric Acid, and Phenothiazine, represent diverse industrial applications creating compliance obligations spanning chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, laboratories, and general industry.
Organizations maintaining NIOSH skin notation profiles compliance must understand both the substance-specific hazard characterizations and the broader methodological shifts, particularly the removal of SI ratio approaches, that influence how skin hazards are assessed under 2026 requirements. This understanding enables targeted compliance responses rather than reactive adjustments following enforcement actions.
The complexity of modern chemical safety compliance exceeds what manual processes can reliably manage. AI compliance management for chemical safety platforms provide the regulatory monitoring, inventory screening, risk prioritization, and documentation management capabilities that sustainable compliance requires. Organizations investing in these capabilities gain competitive advantages while reducing exposure to enforcement actions and operational disruptions.
The 2026 finalization creates urgency for immediate action. Organizations that leverage AI tools for regulatory compliance to assess exposure, identify gaps, and implement remediation now will achieve compliance readiness as enforcement expectations intensify. Those that delay face compressed timelines, elevated costs, and increased enforcement risk as OSHA incorporates finalized profiles into inspection protocols.
Executive leadership must recognize that workplace chemical risk assessment AI capabilities represent strategic infrastructure, not optional technology investments. Building robust compliance systems in 2026 positions organizations to address not only the current NIOSH finalization but ongoing evolution of occupational safety requirements across all jurisdictions where they operate.
Schedule a consultation with Certivo to assess your organization's exposure to finalized NIOSH skin notation requirements and develop AI-powered compliance strategies that protect workers while ensuring operational continuity throughout 2026 and beyond.
Lavanya
Lavanya is an accomplished Product Compliance Engineer with over four years of expertise in global environmental and regulatory frameworks, including REACH, RoHS, Proposition 65, POPs, TSCA, PFAS, CMRT, FMD, and IMDS. A graduate in Chemical Engineering from the KLE Institute, she combines strong technical knowledge with practical compliance management skills across diverse and complex product portfolios.
She has extensive experience in product compliance engineering, ensuring that materials, components, and finished goods consistently meet evolving international regulatory requirements. Her expertise spans BOM analysis, material risk assessments, supplier declaration management, and test report validation to guarantee conformity. Lavanya also plays a key role in design-for-compliance initiatives, guiding engineering teams on regulatory considerations early in the product lifecycle to reduce risks and streamline market access.
Her contributions further extend to compliance documentation, certification readiness, and preparation of customer deliverables, ensuring transparency and accuracy for global stakeholders. She is adept at leveraging compliance tools and databases to efficiently track regulatory changes and implement proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Recognized for her attention to detail, regulatory foresight, and collaborative approach, Lavanya contributes significantly to maintaining product compliance, safeguarding brand integrity, and advancing sustainability goals within dynamic, globally integrated manufacturing environments.

